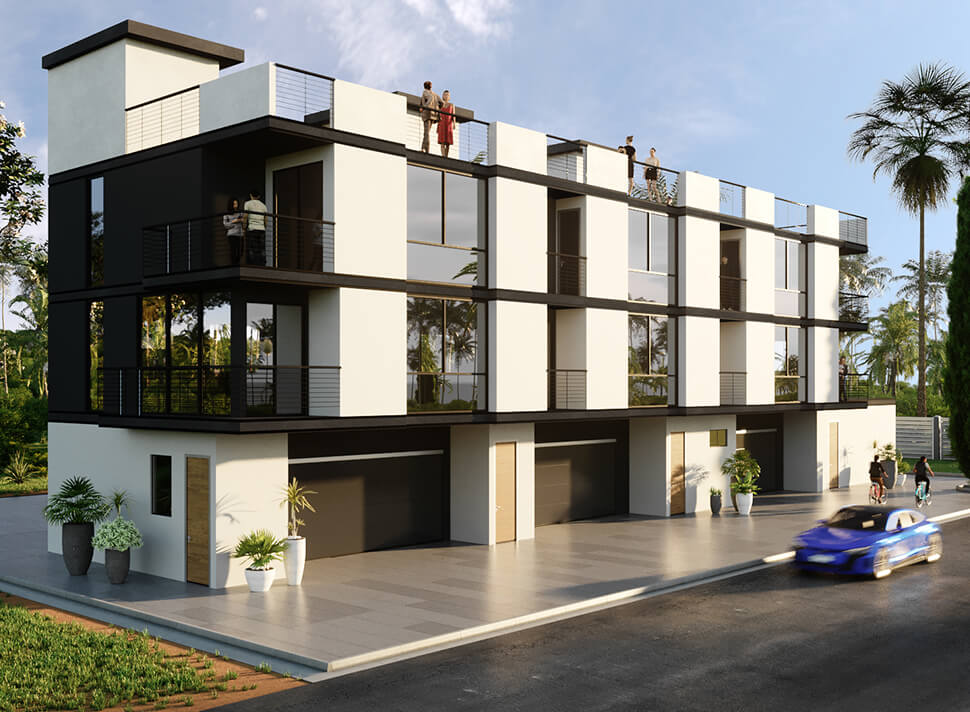
Bringing Products to Life: The Magic of 3D Rendering
Introduction
The landscape of product visualization has undergone a transformative journey, especially with the advent of 3D rendering technologies. Gone are the days when product concepts were limited to sketches and 2D images. Today, 3D rendering stands at the forefront of product design and marketing, offering an immersive experience that bridges the gap between imagination and reality. This article delves into 3D product renderings, exploring its nuances, techniques, and real-world applications that have revolutionized how products are visualized and presented.
The history of product visualization dates back to simple hand-drawn sketches and has evolved through the digital revolution, bringing us to today's sophisticated 3D rendering techniques. This evolution mirrors the advancement of technology and the increasing demand for more realistic, engaging, and interactive product presentations.
The Basics of 3D Rendering
Understanding 3D Rendering
3D rendering is an artistic process akin to photography or cinematography, where you create two-dimensional images or animations from a 3D model. CrafModeln's specialized software defines the model's appearance using textures, colors, and materials. Then, through the rendering process, it's placed in a virtual environment where lighting, camera angles, and other factors are adjusted to create the final image or animation.
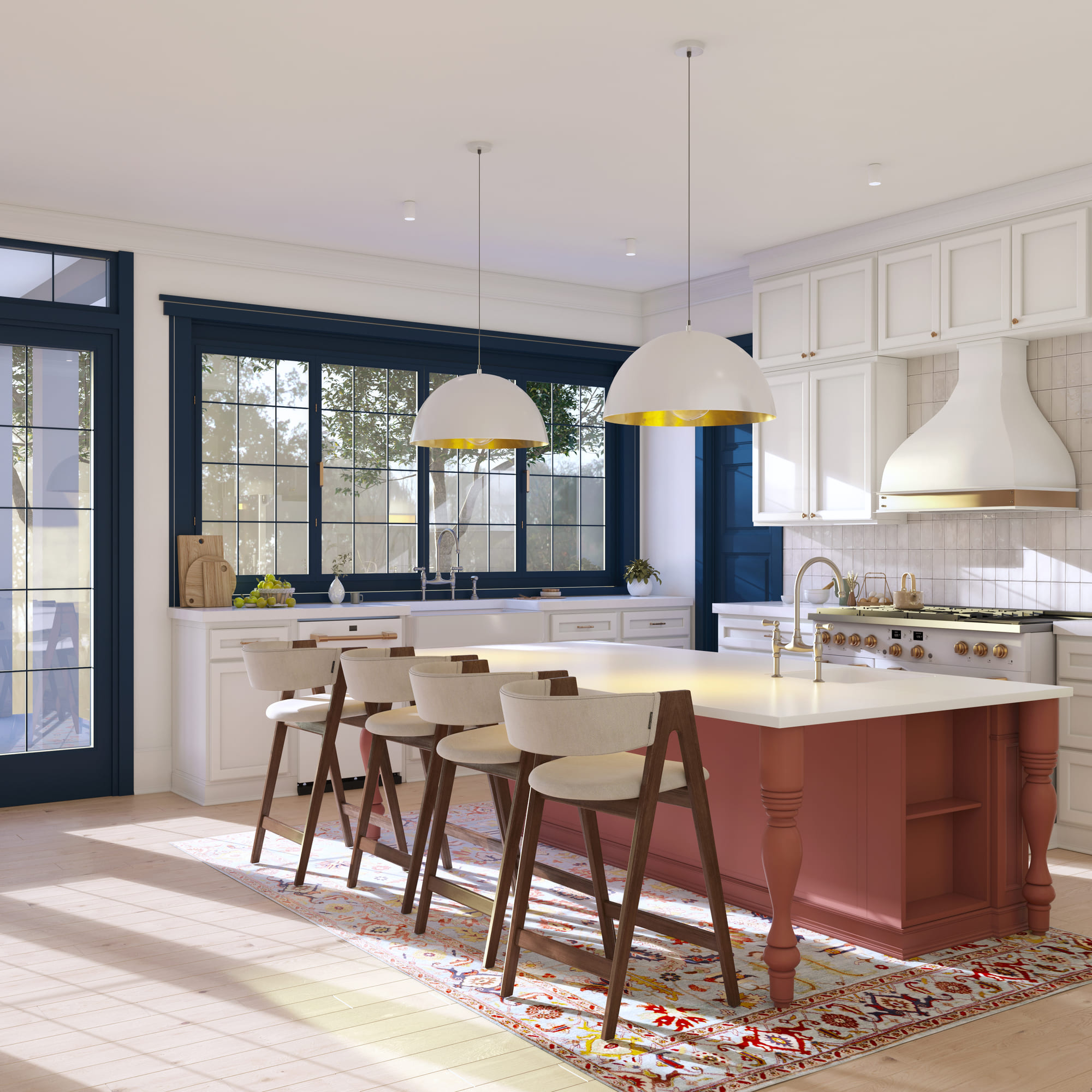

Image from Yousee Studio
This process is pivotal in various fields, from architectural visualization to product design, gaming, and movie production. For instance, architecture allows designers and clients to visualize a building before it's built, considering aspects like lighting at different times of the day and the interaction of other materials. In product design, it provides a realistic preview of the product, which is invaluable for marketing and client presentations.
Different Types of 3D Rendering Techniques
3D rendering encompasses several techniques, each suitable for different needs and outcomes. Real-time rendering is used in video games and interactive simulations, where images must be generated on the fly as the user interacts with the environment. This type of rendering demands a balance between quality and speed to ensure a seamless user experience.
On the other hand, pre-rendering is used when image quality is paramount and time is not a constraint, such as in animations and high-quality visualizations for advertising. This technique produces highly realistic images but requires more processing time.
Tools and Software
The 3D rendering landscape has various software options, offering unique features and capabilities. Autodesk 3ds Max and Maya are popular choices for high-end rendering and are widely used in the film and video game industries. They provide robust modeling, animation, and rendering tools but have a steep learning curve and a high price tag.
For architectural visualization, software like SketchUp and Lumion is preferred for its user-friendly interface and quick rendering capabilities. Blender, an open-source alternative, has gained significant traction for its comprehensive features rivaling expensive commercial software.
When choosing the right tool, it's essential to consider factors like the specific needs of your project, your proficiency in 3D modeling, and your budget. For beginners and small projects, user-friendly and cost-effective software like Blender or SketchUp might be the best choice. However, investing in professional-grade software like 3ds Max or Maya could be worthwhile for more complex and high-quality renderings.
The Design Process
From Concept to 3D MModelThe journey from a mere concept to a 3D model is a meticulous process that involves several stages. Initially, it starts with a conceptual sketch or idea, which is then translated into a 3D model using modeling software. This stage is about building the structure of the model, considering proportions, and ensuring that the design is feasible and structurally sound.
Attention to detail in this phase is crucial. For instance, when creating a 3D model of a new smartphone, designers must consider the exact dimensions, the placement of buttons and cameras, and even the materials to be used for different parts. This detailed planning helps create a visually appealing, accurate, and functional model.
Textures and Materials
The next step after the model is created is to bring it to life with textures and materials. This process involves mapping detailed images (textures) onto the model's surface to give it a realistic appearance. For instance, if you're rendering a leather sofa, you'll apply a leather texture to it, including the color, pattern, and even the way leather reflects light.
Applying textures and materials requires understanding how materials interact with light and the environment. It's a skill that combines artistic vision with technical knowledge. For example, how light interacts with a silk curtain vastly differs from how it interacts with a wooden table. Understanding these nuances is critical to creating realistic renderings.
Lighting plays a pivotal role in the realism of a 3D rendering. It involves placing virtual light sources in the scene to mimic natural or artificial light. Good lighting can highlight the model's best features, create mood, and add depth to the image.
For example, in architectural rendering, the lighting setup can showcase how a building looks under different lighting conditions, like the warm glow of sunset or the bright light of midday. Lighting techniques vary widely, from simple point lights to complex global illumination, which simulates how light bounces around a scene, creating soft shadows and color bleeding.
The rendering process is the final step, where the computer calculates and produces the final image or animation. This involves computing how light interacts with the materials and objects in the scene based on the rendering settings.
These settings determine the quality of the final image and the time it will take to render. High-quality settings can produce stunningly realistic images but might take hours or even days to generate. On the other hand, lower settings render faster but at the cost of image quality.
Balancing quality and rendering time is a crucial skill in 3D rendering. It's about understanding the purpose of the rendering and the level of detail required. A lower quality is sufficient for quick client presentations, but you opt for the highest quality for final marketing materials.
The design and rendering processes in 3D visualization are intricate and multifaceted, demanding a balance of artistic talent and technical skill. As we delve deeper into advanced techniques and trends in the following sections, the complex tapestry of 3D rendering will unfold, revealing its profound impact on various industries and its potential to shape the future of product visualization.
Advanced Techniques and Trends
Animation and Interactive Elements
The realm of 3D rendering is not just limited to still images. Animation and interactive elements have brought a new dimension to how products are presented and experienced. In the context of product design, animation can demonstrate the functionality of a product, show how parts move and interact, or provide a 360-degree view. For example, a car manufacturer might use animation to show how the suspension system of a vehicle works, providing a more precise understanding to the consumer.
Interactive 3D models have gained popularity in e-commerce and marketing. These models allow users to interact virtually with the product by rotating, zooming, and customizing features like color or components. This interactivity enhances the user experience and gives customers a more detailed view of the product, potentially influencing their purchasing decisions. According to a study by Shopify, interactive 3D models are shown to increase conversion rates by up to 250%.
Emerging Trends in 3D Rendering
3D rendering is continuously evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging regularly. One significant trend is using AI and machine learning in rendering processes. AI algorithms can significantly reduce rendering times, making high-quality renders more accessible and cost-effective. For instance, NVIDIA's AI-based rendering technology, known as Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS), utilizes deep learning to produce images that look like a traditional high-resolution render but with a fraction of the computational power and time.
Another trend is the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) with 3D rendering. This integration offers an immersive experience, allowing users to explore a product or space in a virtual environment. For example, IKEA's AR app, IKEA Place, will enable users to place virtual furniture in their homes, providing a realistic view of how the product would fit and look in their space.
Furthermore, sustainability in 3D rendering is gaining traction, with more companies seeking eco-friendly practices in their design and rendering processes. This includes optimizing rendering workflows to consume less energy and using software that supports more efficient rendering techniques.
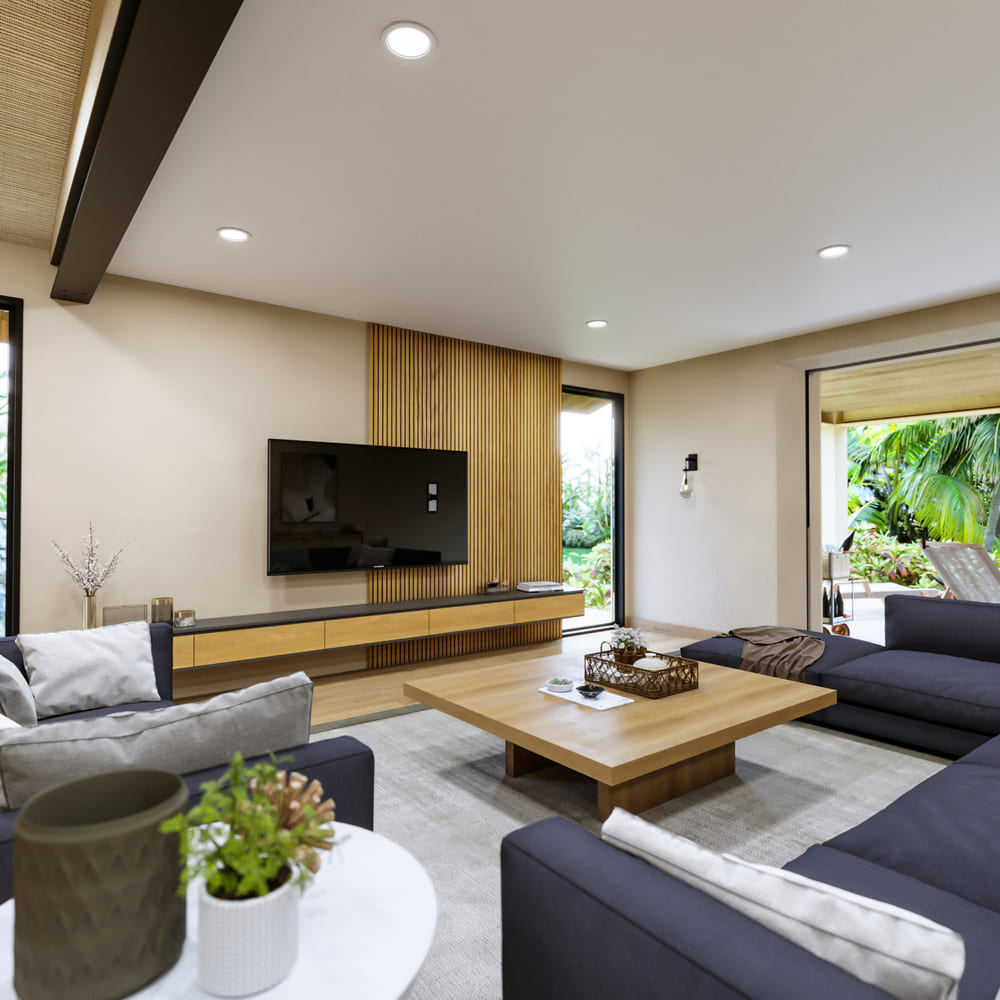

Image from Yousee Studio
Real-World Applications
Case Studies: Successful 3D Renderings
The practical application of 3D rendering spans various industries, and analyzing successful case studies provides insights into its effectiveness and versatility.
- Automotive Industry: BMW, for instance, uses 3D rendering not just for design and prototyping, marketing, and sales. Their BMW I Visualizer allows customers to configure and view their cars in high-quality 3D on their devices. This tool has enhanced customer engagement and provided a more interactive and personalized shopping experience.
- Architecture and Real Estate: In real estate, 3D renderings showcase properties before they are built. The visualization firm, The Boundary, specializes in photorealistic renderings and animations for luxury real estate. Their work lets potential buyers visualize properties in great detail, contributing to successful sales even before construction.
Industry Impact
The impact of 3D rendering is profound across various sectors. In product design and manufacturing, it reduces the need for physical prototypes, saving time and resources. Companies can test and modify designs virtually, leading to more efficient development cycles. According to a report by the Aberdeen Group, companies incorporating 3D rendering and virtual prototyping enjoy a 50% reduction in physical prototypes, leading to a 60% decrease in time-to-market.
In advertising and marketing, 3D renderings provide a flexible and cost-effective way to create high-quality visuals. Instead of expensive photo shoots, companies can produce stunning images and animations of their products in different settings and configurations. This flexibility is invaluable, especially when marketing products internationally, as it allows for easy adaptation to other markets and preferences.
In architecture, 3D rendering has revolutionized client presentations and marketing materials. Architects can now present realistic and detailed visualizations of their designs, making it easier for clients to understand and appreciate the proposed work. This visual clarity often leads to quicker decision-making and approval processes.
3D renderings and animations create more engaging and informative materials for education and training. For example, in medical training, detailed 3D models of the human body are used to teach anatomy, providing a mor interactive and immersive learning experience than traditional methods.
The influence of 3D rendering is also evident in the entertainment industry, particularly in film and gaming, where it is used to create stunning visual effects and immersive virtual worlds. Movies like "Avatar" and games like "The Witcher 3" show how 3D rendering can create captivating and lifelike experiences.
The future of 3D rendering in product visualization is bright, with continuous advancements in technology making it more accessible, efficient, and versatile. Its ability to enhance product design, streamline development processes, and create engaging marketing experiences makes it an invaluable tool in the modern digital landscape.
Conclusion
The journey through the world of 3D rendering has revealed its transformative impact across various industries, from product design and real estate to entertainment and education. Once a niche and expensive tool, this technology has become a cornerstone in modern visualization, design, and marketing strategies. The conclusion aims to encapsulate the essence of 3D rendering, its current and future implications, and why it's more than just a technological advancement—it's a pivotal shift in how we perceive, interact with, and market products and ideas.
Summarizing the Importance and Impact of 3D Rendering
The importance of 3D rendering can be encapsulated in several vital points:
- Enhanced Realism and Precision: 3D rendering offers realism and detail unattainable through traditional 2D images or even physical prototypes. This precision is not just aesthetic but functional, allowing designers and engineers to test and refine their concepts accurately. For instance, in the automotive industry, companies like Audi use 3D rendering to create detailed prototypes of new car models, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming physical prototypes.
- Cost-Effective and Time-Efficient: The adoption of 3D rendering has shown to be cost-effective, especially in reducing the need for physical prototypes and expensive photo shoots. For example, Nike uses 3D rendering to design and visualize their products, significantly reducing costs associated with traditional photography and prototyping. According to a case study, this approach has reduced their time-to-market by 50% and decreased their photography costs by 75%.
- Market Adaptability and International Appeal: 3D-rendered images and animations can be easily adapted for different markets, enhancing their international appeal. This adaptability is crucial in today’s global market, where consumer preferences vary widely across regions. Brands like IKEA have leveraged 3D rendering to create catalogs tailored to different cultural contexts, demonstrating the versatility of this technology in global marketing.
- Interactive and Engaging Customer Experiences: Integrating 3D rendering with interactive technologies like AR and VR has revolutionized customer engagement. By providing immersive and interactive experiences, companies can better engage with their customers, leading to higher satisfaction and increased sales. A study by Deloitte found that AR and VR are expected to grow into a $1.5 billion market by 2025, highlighting the potential of these technologies in conjunction with 3D rendering.
Embracing 3D Technology in Product Development
The future of product development and marketing is inextricably linked to the advancements in 3D rendering technology. Companies that embrace this technology can expect several benefits:
- Innovation in Product Design: 3D rendering allows for more creative freedom and experimentation in product design. Designers can easily explore different concepts and iterations, pushing the boundaries of innovation. The tech giant Apple, for example, extensively uses 3D rendering in the design process of its products, enabling it to create iconic, cutting-edge designs.
- Improved Collaboration and Communication: 3D rendering facilitates better collaboration and communication among teams and clients. Providing a clear visual representation reduces misunderstandings and speeds up the decision-making process. In architecture, firms like Zaha Hadid Architects use 3D rendering not just for client presentations but also as a tool for collaboration within their design teams.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, 3D rendering offers an eco-friendly alternative to physical prototypes and traditional marketing materials. Reducing the need for biological materials and transportation minimizes the environmental footprint of the design and marketing processes.
Looking to the Future
As we look to the future, it’s clear that 3D rendering will continue to evolve and shape various sectors. Integrating AI and machine learning is poised to revolutionize rendering processes, making them faster and more efficient. The continual development of VR and AR technologies will further enhance the immersive experiences that 3D rendering can provide.
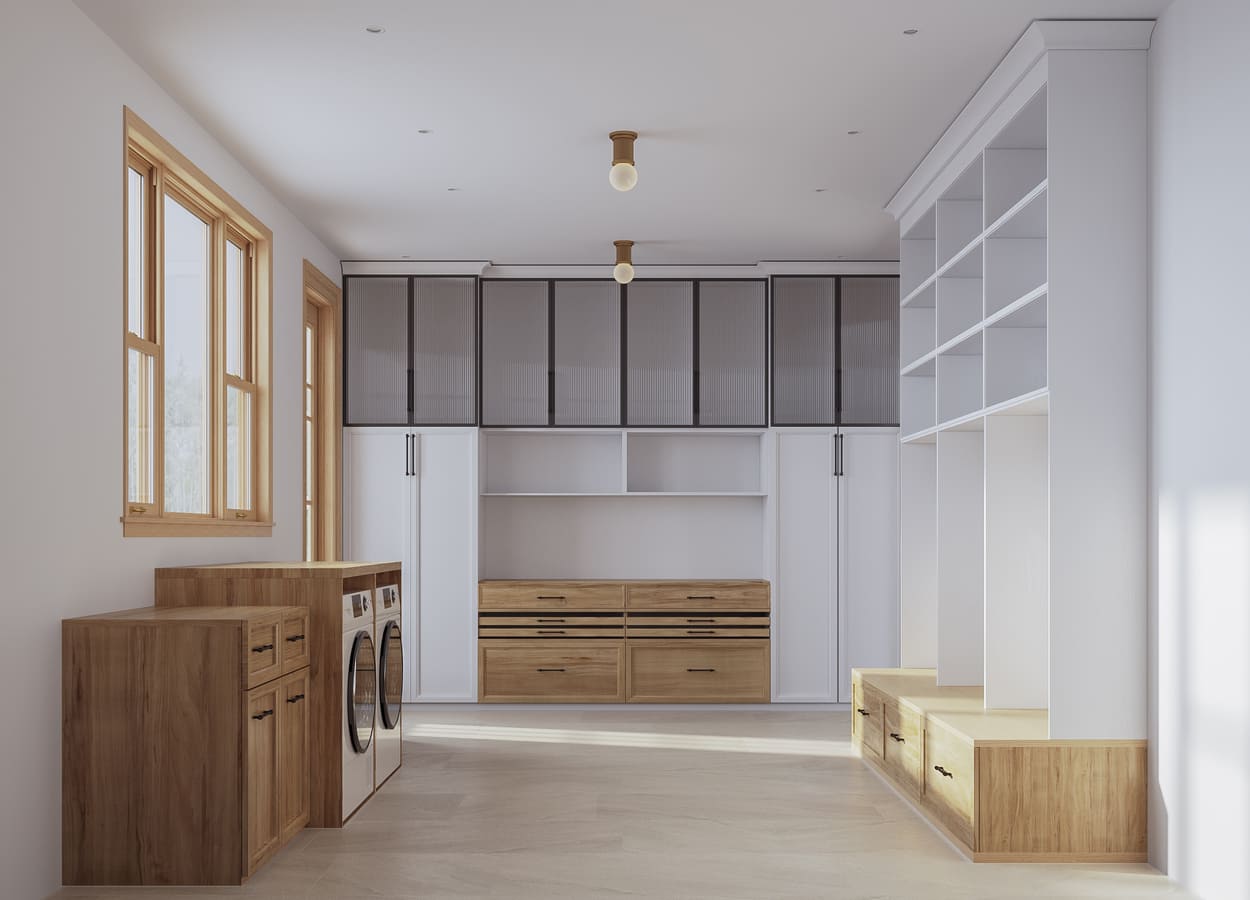

Image from Yousee Studio
The potential for 3D rendering to contribute to sustainable practices is also significant. With the increasing focus on environmental impact, the ability of 3D rendering to reduce waste and resource usage positions it as a vital tool in sustainable design and marketing strategies.
In conclusion, 3D rendering is not just a tool but a gateway to a new era of visualization, design, and interaction. Its impact spans beyond the confines of individual industries, influencing how we think about and interact with products and spaces. As this technology continues to advance, it will undoubtedly unlock new possibilities, driving innovation, efficiency, and sustainability in the future.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Ray Lisbon is a content writer and the author of this article.