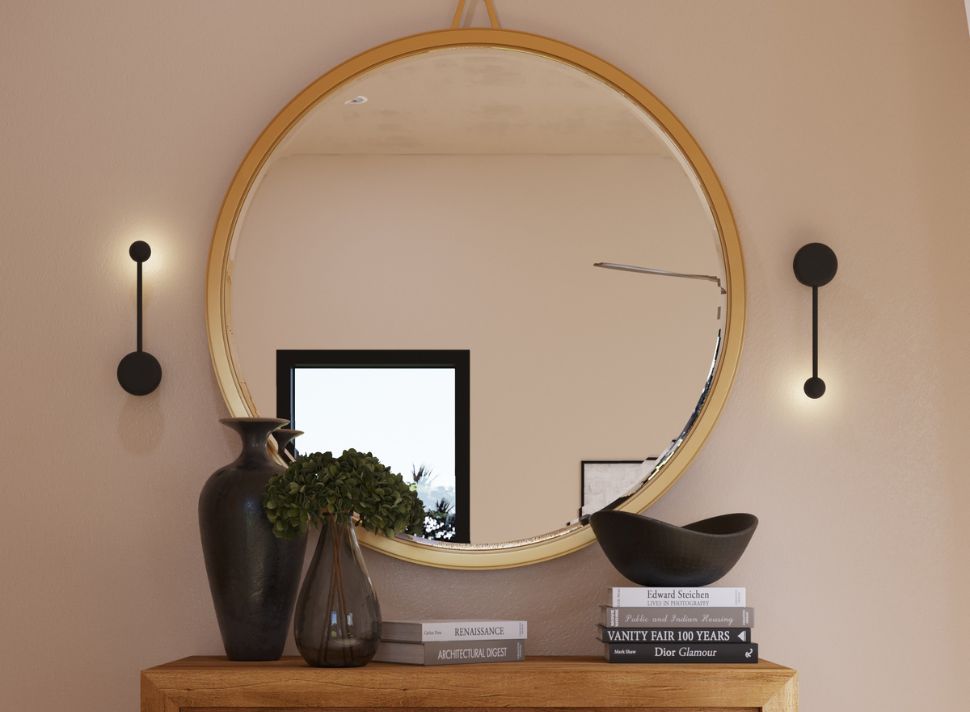
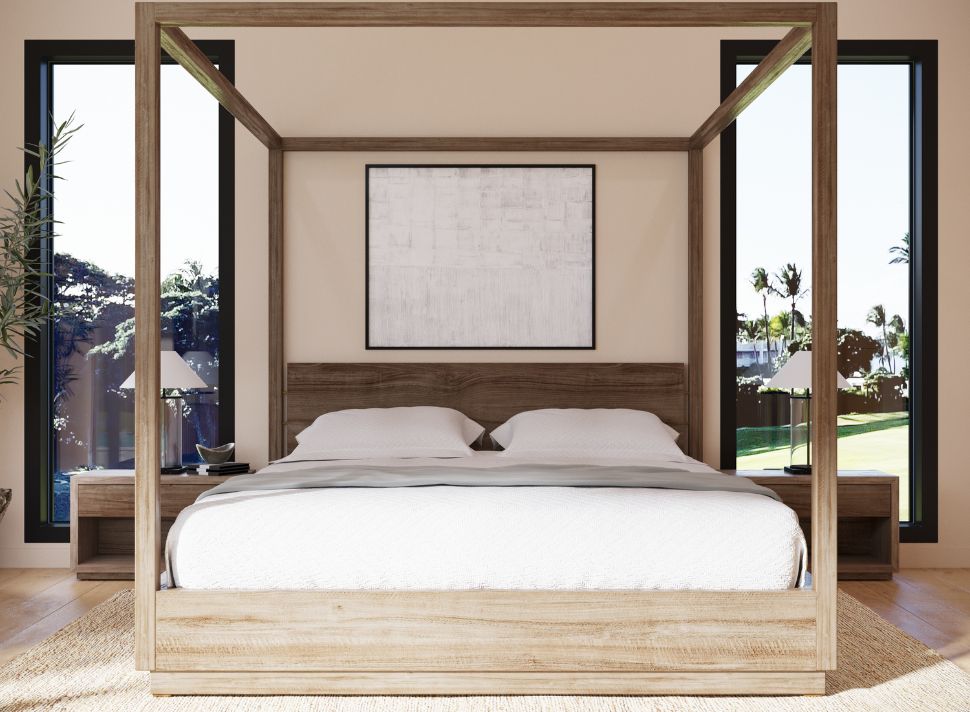
The Visual Revolution: Exploring the World of 3D Product Rendering
Introduction
3D product rendering has marked a new era in product design and visualization. This technology has revolutionized how products are conceptualized and presented and reshaped the interaction between creators and consumers. This article delves into the evolution, techniques, and significant impact of 3D product renderings. We explore how it has transformed traditional design methodologies, enhanced consumer experiences, and opened up new possibilities in various industries, from real estate to fashion and beyond.
Historical Evolution of Product Rendering
From Traditional Methods to Digital Transformation
Traditionally, product rendering was a manual and time-intensive process. Artists and designers relied on sketches and physical models to visualize and present their ideas. While artistic, this method offered limited flexibility and was often constrained by the available materials and tools. The digital transformation in design, however, marked a significant shift. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) in the 1960s changed the landscape, paving the way for more advanced forms of digital rendering.
The Advent of 3D Rendering in Product Design
The real turning point in product rendering came with the advent of 3D modeling and rendering software in the late 20th century. This technology allowed designers to create detailed, three-dimensional representations of products on computers, offering unprecedented detail and realism. One of the early pioneers in this field was the software SketchUp, initially developed in 2000. It provided a user-friendly platform for 3D modeling, which was a significant step forward from the more technical and less intuitive CAD programs of the time.
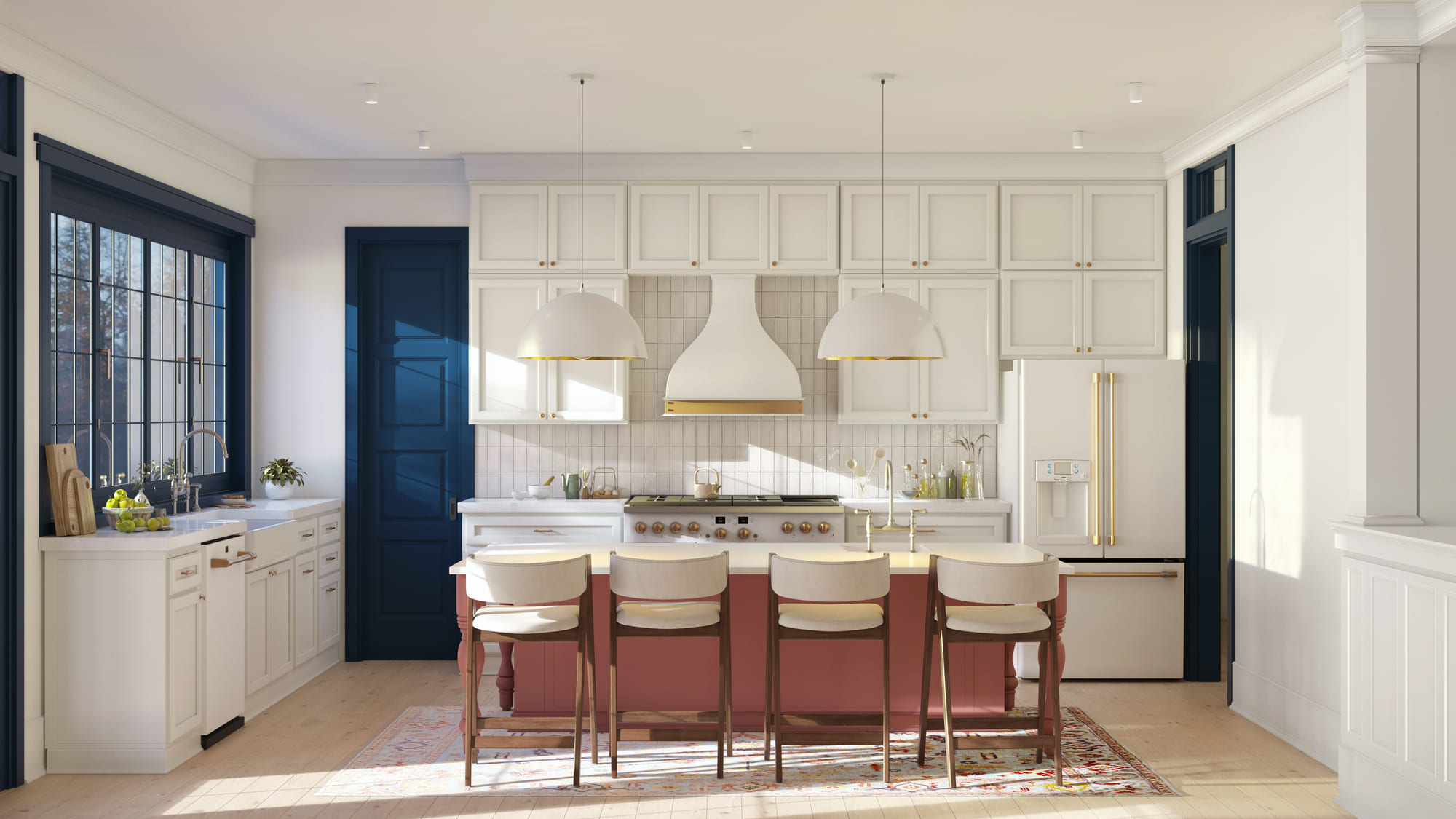

Image from Yousee Studio
Transition to Mainstream and Adoption Across Industries
As 3D rendering software became more sophisticated and user-friendly, its adoption spread rapidly across various industries. Autodesk's 3ds Max launched in 1996, became a staple in the gaming, film, and architecture industries for its powerful rendering capabilities. Similarly, Adobe's Photoshop extended its capabilities beyond photo editing to include 3D rendering features, making it a versatile tool for designers in various fields.
Core Principles and Techniques of 3D Product Rendering
Understanding the Basics of 3D Rendering
3D product rendering is based on creating digital models in a three-dimensional space. These models are then textured, lit, and rendered to produce images or animations that can depict realistic or artistic representations of the product. The process involves a deep understanding of light, shadow, material properties, and camera angles, all contributing to the outcome.
Essential Techniques and Technologies in 3D Product Rendering
Several vital techniques are fundamental in 3D product rendering. One of the most important is texturing, which involves applying detailed surfaces to the 3D models. This can include anything from simple colors to complex patterns and realistic material appearances. Lighting is another crucial aspect, as it defines how shadows and highlights interact with the model, significantly affecting its realism.
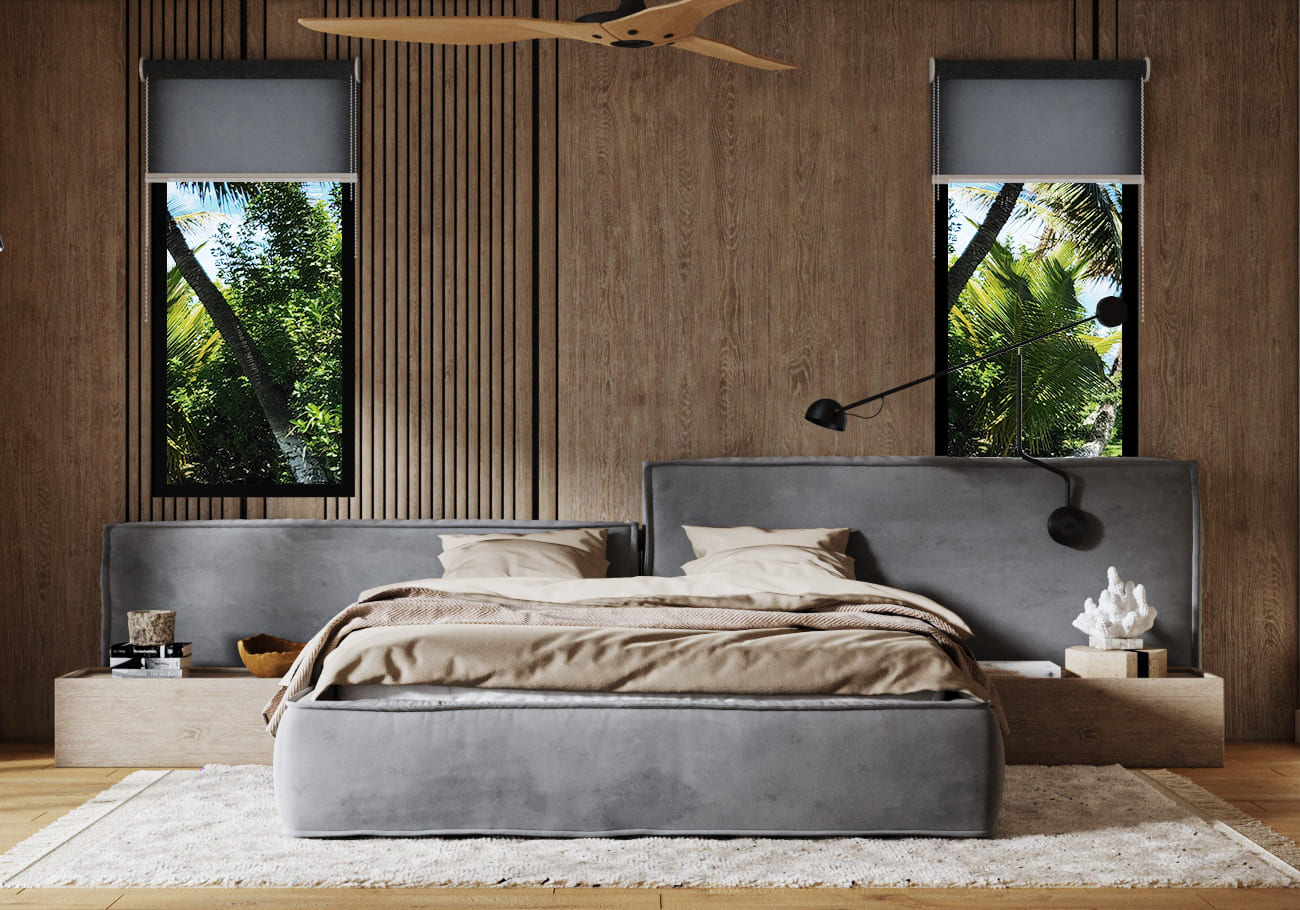

Image from Yousee Studio
Modern 3D rendering software offers many tools and features to support these techniques. For example, Ray tracing, a rendering method that simulates the way light interacts with objects, is used to achieve photorealistic effects. For instance, NVIDIA's RTX technology has made real-time ray tracing a reality, significantly reducing rendering times.
Real-World Applications and Impact
3D product rendering has found extensive application in sectors such as real estate, where it is used for creating lifelike representations of properties for marketing and client presentations. In product design, companies use 3D rendering to visualize products before they are manufactured, allowing for adjustments and improvements at minimal costs.
The Impact of 3D Rendering on Various Industries
The influence of 3D product rendering extends far beyond the confines of traditional design industries. It has become a vital tool across various sectors, fundamentally altering how products are developed, marketed, and experienced by consumers.
Application and Influence in Automotive, Fashion, and Architecture
In the automotive industry, 3D rendering is critical in design and marketing. Car manufacturers like Tesla and BMW use 3D models to conceptualize and refine designs before any physical prototype is built. This approach saves time and resources and enables designers to experiment with different designs and features quickly. For marketing, these renders create stunning visuals and interactive models for customers, allowing them to customize and visualize their vehicles in detail before purchase. This level of interaction was previously unattainable, enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction.
The fashion industry has also embraced 3D rendering, particularly in e-commerce. Brands like Nike and Adidas use 3D models to showcase their products online, giving customers a more detailed and realistic view of items. This technology has also revolutionized the design process in fashion, where designers can create and alter their designs digitally. It allows for rapid prototyping, testing different materials and styles without needing physical samples, thus speeding up the design process and reducing waste.
Architecture and real estate have seen the most dramatic impact from 3D rendering. Architects use 3D models to visualize and present their designs in realistic settings, allowing clients to understand and experience the space before it is built. This capability is a powerful sales tool and aids in the design process, helping architects and clients make more informed decisions. Real estate agents and developers use 3D renderings and virtual tours to market properties, providing potential buyers with immersive experiences of homes or commercial spaces, especially useful for off-plan properties.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Transformative Examples
The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the world’s tallest building, is a prime example of the power of 3D rendering in architecture. During its design phase, 3D models were extensively used to simulate the building’s appearance, structure, and the impact of environmental factors. This process was crucial in solving design challenges and achieving the architectural marvel it is today.
In the automotive industry, Audi’s use of 3D rendering to design and market its cars stands out. The company uses sophisticated 3D models to create vehicles, allowing for high detail and accuracy. These models are also used in their online configurator, where customers can customize their car, changing colors, wheels, and other features while viewing a realistic 3D representation of their choices.
Challenges and Innovations in 3D Product Rendering
Despite its many advantages, 3D product rendering has challenges. These challenges spur continuous innovation in the field, driving the development of new technologies and techniques.
Technical and Creative Challenges in 3D Rendering
One of the primary challenges in 3D rendering is achieving photorealism. Creating renders indistinguishable from real photos requires a deep understanding of lighting, materials, and camera settings. It also demands high computational power to process complex scenes with realistic textures, reflections, and shadows.
Another challenge is the time and expertise required to create high-quality 3D models. Detailed models can take significant time to build and render, requiring skilled professionals. This can be a barrier for smaller companies or individual designers needing more resources or expertise to create such detailed models.
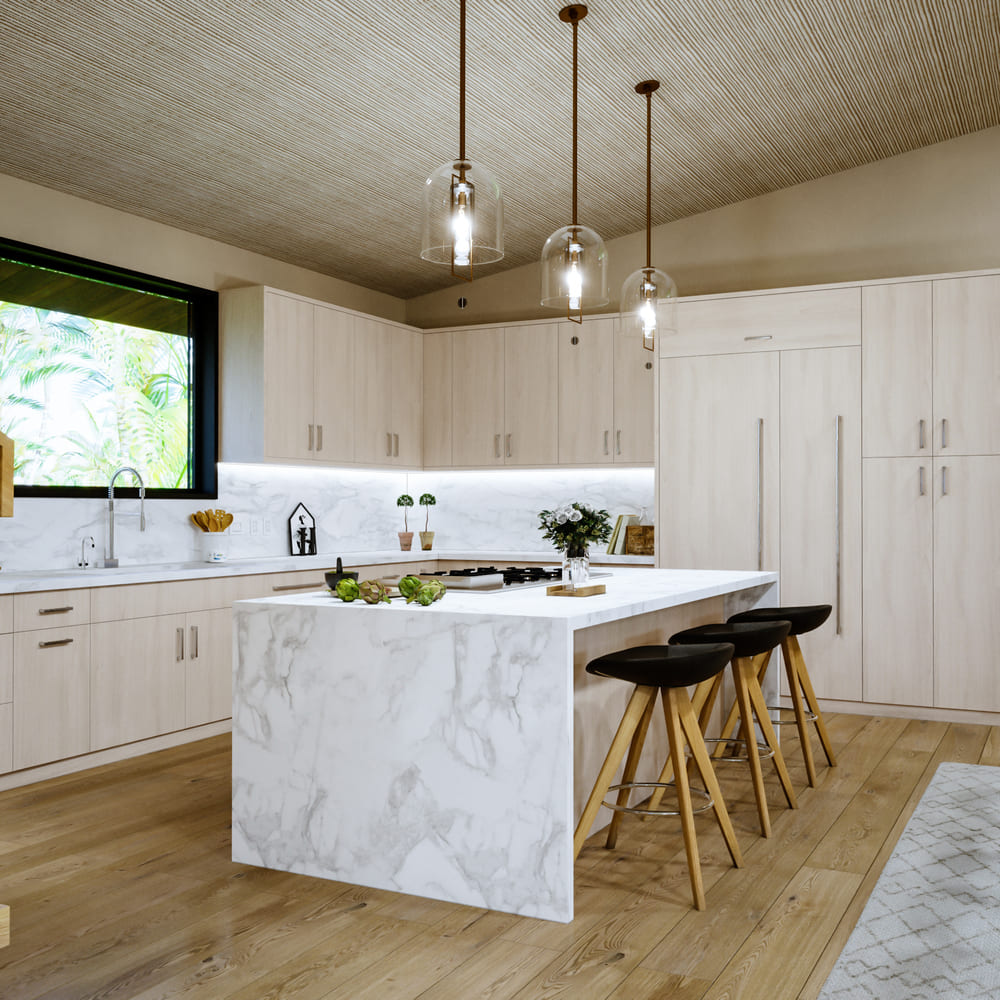

Image from Yousee Studio
Cutting-edge Innovations and Future Trends in Rendering Technology
Addressing these challenges has led to several innovations in 3D rendering technology. One significant advancement is the development of real-time rendering engines, such as Unreal Engine and Unity. These engines allow designers to view and interact with their models in real time, significantly reducing the time it takes to produce final renders.
Another innovation is the use of AI in rendering software. AI algorithms are being developed to automate various aspects of the rendering process, such as optimizing lighting and textures, which can help achieve photorealism more efficiently.
Looking to the future, we expect to see continued advancements in rendering technology. One potential area is virtual and augmented reality integration, which could provide even more immersive experiences. As these technologies evolve, they will likely become more accessible, opening up 3D rendering to a broader range of users and applications.
The impact of 3D rendering in various industries has been profound, offering new ways to design, visualize, and market products. While challenges remain, continuous technological innovations are pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with 3D rendering. The future of this field is undoubtedly bright, with endless possibilities for creativity and innovation.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of the world of 3D product rendering, it's evident that this technology has ushered in a visual revolution, redefining the boundaries of design, marketing, and customer engagement across various industries. The journey from traditional rendering methods to today's sophisticated 3D visualization techniques highlights a remarkable evolution that has transformed ideas into vivid, tangible experiences.
Recap of the Transformative Role of 3D Product Rendering
The transformative role of 3D product rendering cannot be overstated. Automotive design has enabled a more efficient, creative, and customer-centric approach to vehicle development and marketing. In fashion, it has revolutionized the design process, allowing for rapid prototyping and a significant waste reduction. In architecture and real estate, 3D rendering has become an indispensable tool for visualizing and marketing properties, enhancing both the design process and the buying experience.
Future Prospects and the Ongoing Evolution in 3D Rendering
Looking ahead, the future of 3D product rendering is bright with prospects. The ongoing evolution of this technology, fueled by advancements in AI, real-time rendering, and virtual and augmented reality, promises to enhance its capabilities further. We can anticipate more intuitive and efficient rendering processes, greater accessibility for a broader range of users, and even more immersive and interactive experiences for clients and consumers.
3D product rendering stands at the forefront of the digital revolution, a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of advancement in technology and artistry. Its impact spans industries, breaking down traditional barriers and opening new horizons for creativity and innovation. For professionals in design, architecture, real estate, and beyond, mastering this technology is no longer just an asset; it's necessary to stay relevant in an ever-evolving, visually driven world.
In conclusion, 3D product rendering is more than just a tool; it's a gateway to new possibilities, a means to bring visions to life, and a crucial element in modern design and visualization narrative. As we continue to push the limits of what can be achieved with this technology, one thing remains clear: the visual revolution is here and reshaping the world as we know it.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Karen Spacey is a content writer and the author of this article.