The Detail in the Design: Mastering 3D Product Rendering
Introduction to 3D Product Rendering
In digital design and marketing, the power of a 3D rendering product cannot be overstated. This cutting-edge technique transcends traditional visual boundaries, offering a depth of realism and detail that elevates product presentation to an art form. At its core, 3D product rendering is the digital craftsmanship of creating lifelike images of products using sophisticated software and tools. It's a process that blends art with technology, enabling designers to construct detailed models that can be viewed, analyzed, and appreciated from any angle. This article explores the nuances of mastering 3D product rendering, focusing on the intricate details that make digital models indistinguishable from their physical counterparts. From the meticulous modeling techniques to the subtle play of light and shadow, we delve into the elements that bring virtual creations to life.
Critical Techniques for High-Quality Renders
Creating high-quality 3D renders goes beyond basic modeling; it's about infusing each model with a level of detail that mimics reality to the closest degree. The foundation of any exceptional 3D render lies in its geometry. Complex techniques such as polygonal modeling, NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-splines), and subdivision surfaces are employed to create detailed and accurate shapes. For instance, in architectural rendering, the precision in modeling textures like brickwork, glass reflections, and landscaping details can significantly impact the overall realism of the scene. Each vertex, edge, and face in the model must be carefully crafted and positioned to reflect the true character of the design.
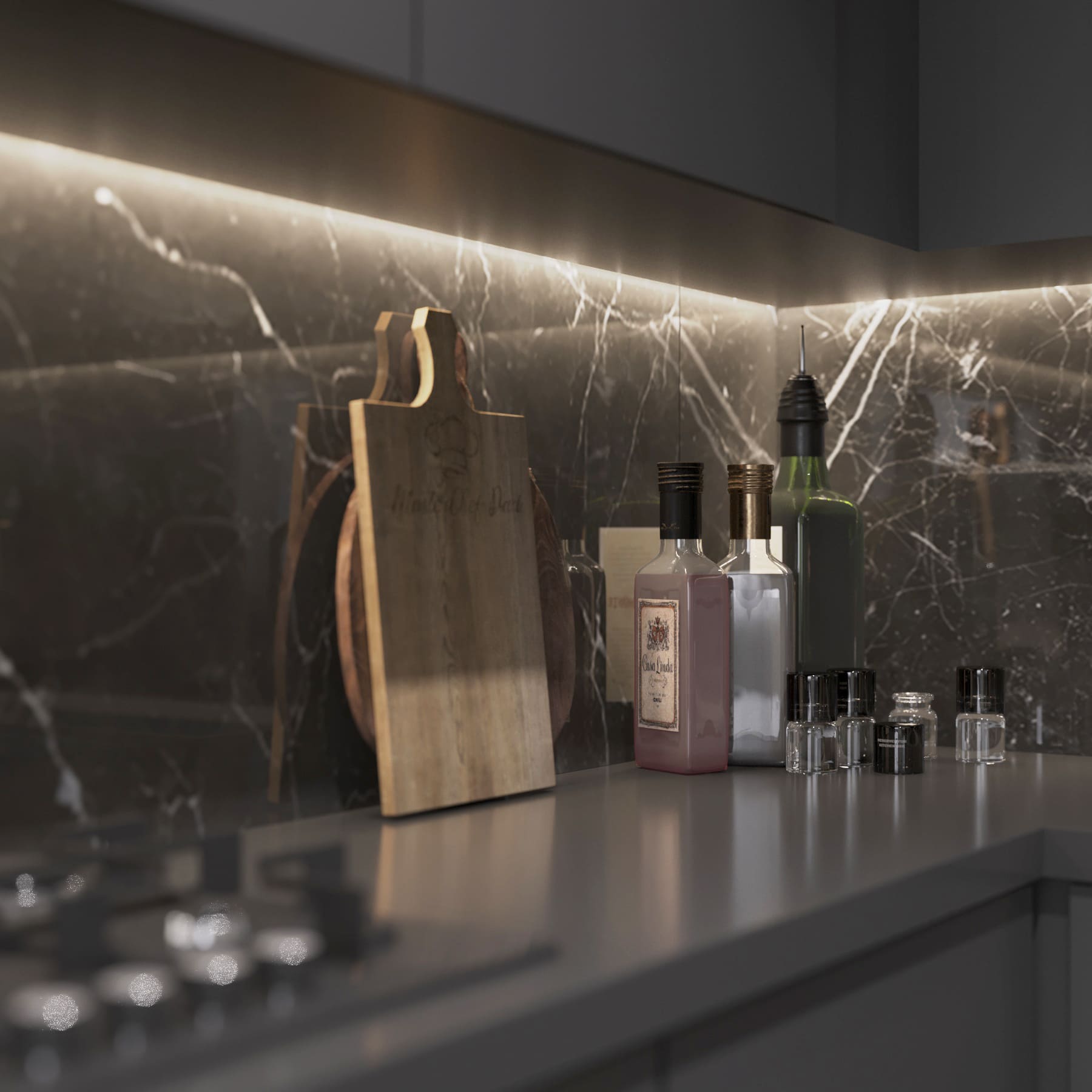

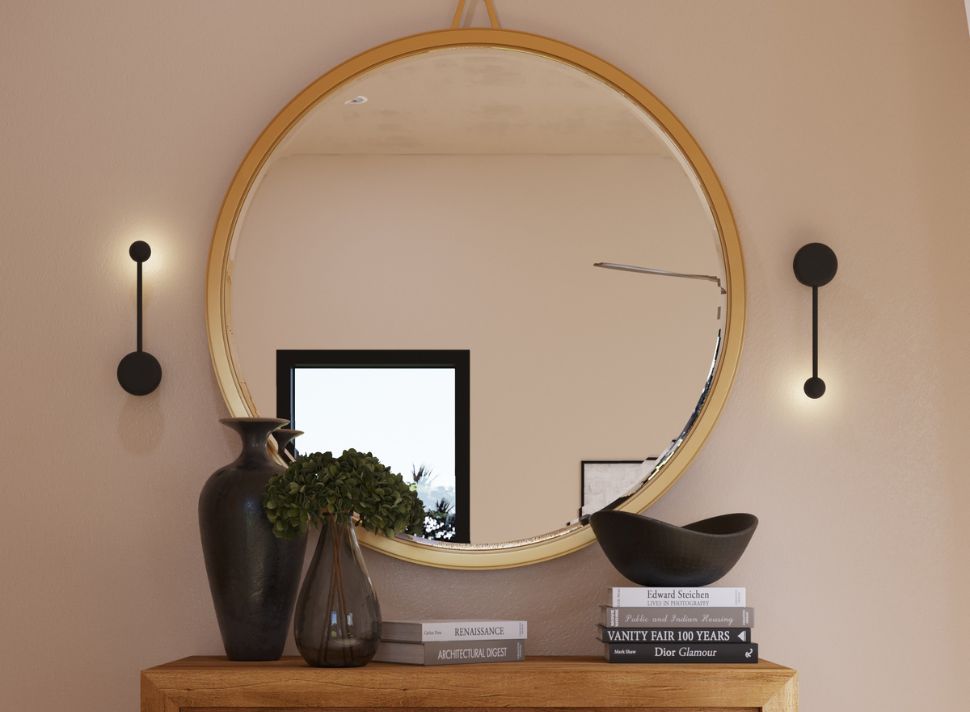
Image from Yousee Studio
Texture mapping takes this realism a step further. It involves applying high-resolution images to the surface of 3D models to simulate real-world materials. The challenge here is choosing the right textures and adjusting the scale, orientation, and variation to avoid repetitive patterns that can break the illusion of reality. Advanced techniques like bump mapping and displacement mapping are used to simulate surface irregularities and details without excessively increasing the model's complexity.
Lighting and shading are pivotal in perceiving depth and material properties in a 3D render. How light interacts with surfaces can convey a lot about the texture, weight, and quality of materials. Photorealistic rendering engines like V-Ray and Corona Renderer offer advanced features such as Global Illumination, which simulates the complex interactions of light in a scene, including reflections, refractions, and shadows. The skillful manipulation of light sources, intensity, and color temperature can dramatically enhance the realism of a render, making objects appear solid, tactile, and grounded in their environment.
Shading techniques, particularly those that simulate the micro-surface detail of materials, are crucial for adding realism. Physically Based Rendering (PBR) workflows have become a standard in the industry, providing a framework for creating materials that react to light predictably and realistically. PBR shaders consider metallicity, roughness, and anisotropy, enabling artists to craft surfaces that accurately reflect, absorb, or diffuse light based on their real-world counterparts.
Software and Tools for Mastering Detail
The selection of software and tools is paramount in 3D product rendering, as they furnish the digital artisan with the capabilities to model, texture, light, and render with unparalleled precision and realism. At the forefront of this digital toolbox are industry-standard software suites such as Autodesk 3ds Max, Maya, and Blender, each offering unique features tailored to various aspects of 3D rendering. Autodesk 3ds Max is renowned for its robust modeling capabilities and extensive plugin ecosystem, making it a favorite among professionals for architectural and Product visualizations. Maya excels in animation and has powerful rendering capabilities, particularly when paired with the Arnold rendering engine, making it ideal for dynamic product demonstrations. With its recent updates and the inclusion of the Eevee real-time render engine, Blender has surged in popularity due to its comprehensive feature set and the advantage of being open-source.
The mastery of these tools extends beyond mere proficiency; it involves an in-depth understanding of their advanced features, such as particle systems for simulating realistic environmental effects, physics engines for creating dynamic animations, and node-based material systems that offer granular control over textures and shaders. Leveraging these features can dramatically enhance the detail and realism of 3D renders, enabling artists to create complex scenes with lifelike materials and lighting.
Furthermore, specialized software such as Substance Painter and Designer by Adobe offers advanced texturing capabilities that are pivotal for adding minute details to 3D models. Substance Painter allows for the painting of textures directly onto 3D models with real-time feedback, enabling the creation of intricate details like wear and tear, scratches, and dirt, which contribute to the realism of the render. Substance Designer offers a node-based interface for creating custom textures procedurally, which can be particularly useful for surfaces that require complex, repeating patterns, such as fabrics, tiles, and natural materials.
Integrating these tools into a cohesive workflow is essential for mastering detail in 3D product rendering. This often involves moving between different software, utilizing the strengths of each to achieve the desired outcome. For example, a typical workflow might involve:
- Modeling in 3ds Max.
- Texturing in Substance Painter.
- Animating in Maya.
- Rendering with a high-fidelity render engine like V-Ray or Corona Renderer.
Each of these tools uniquely contributes to the final render, and the ability to seamlessly integrate their outputs is a hallmark of mastery in 3D rendering.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
The practical application of detailed 3D product rendering spans various industries, each leveraging the technology to enhance visualization, design, and marketing efforts. In the consumer electronics sector, companies such as Apple and Samsung utilize high-detail 3D renders to showcase their products in marketing materials, offering a pristine view of each Product's design and features. The meticulous attention to detail in these renders, from the texture of the materials to the reflection on the screens, plays a crucial role in conveying the quality and sophistication of the products, thereby influencing consumer perception and decision-making.
In the automotive industry, high-detail 3D renders are used for marketing purposes and throughout the design and development process. Companies like BMW and Tesla employ 3D rendering to visualize prototypes long before they are physically built, allowing for a thorough evaluation of aesthetics and functionality. These renders often include intricate details such as the stitching on the seats, the texture of the dashboard materials, and the reflection of light on the car's body, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's design.
Furthermore, interactive 3D renders enable customers to customize their vehicle online, selecting colors, finishes, and accessories, enhancing the buying experience and fostering a deeper connection with the brand.
3D rendering has revolutionized how projects are presented and visualized in architecture and interior design. High-detail renders allow architects and designers to convey their vision with stunning realism, showcasing how light interacts with the materials, the textures of the surfaces, and the spatial relationships within the design. This level of detail not only aids in the decision-making process for clients and stakeholders but also serves as a powerful marketing tool, enabling firms to showcase their projects in the best possible light.
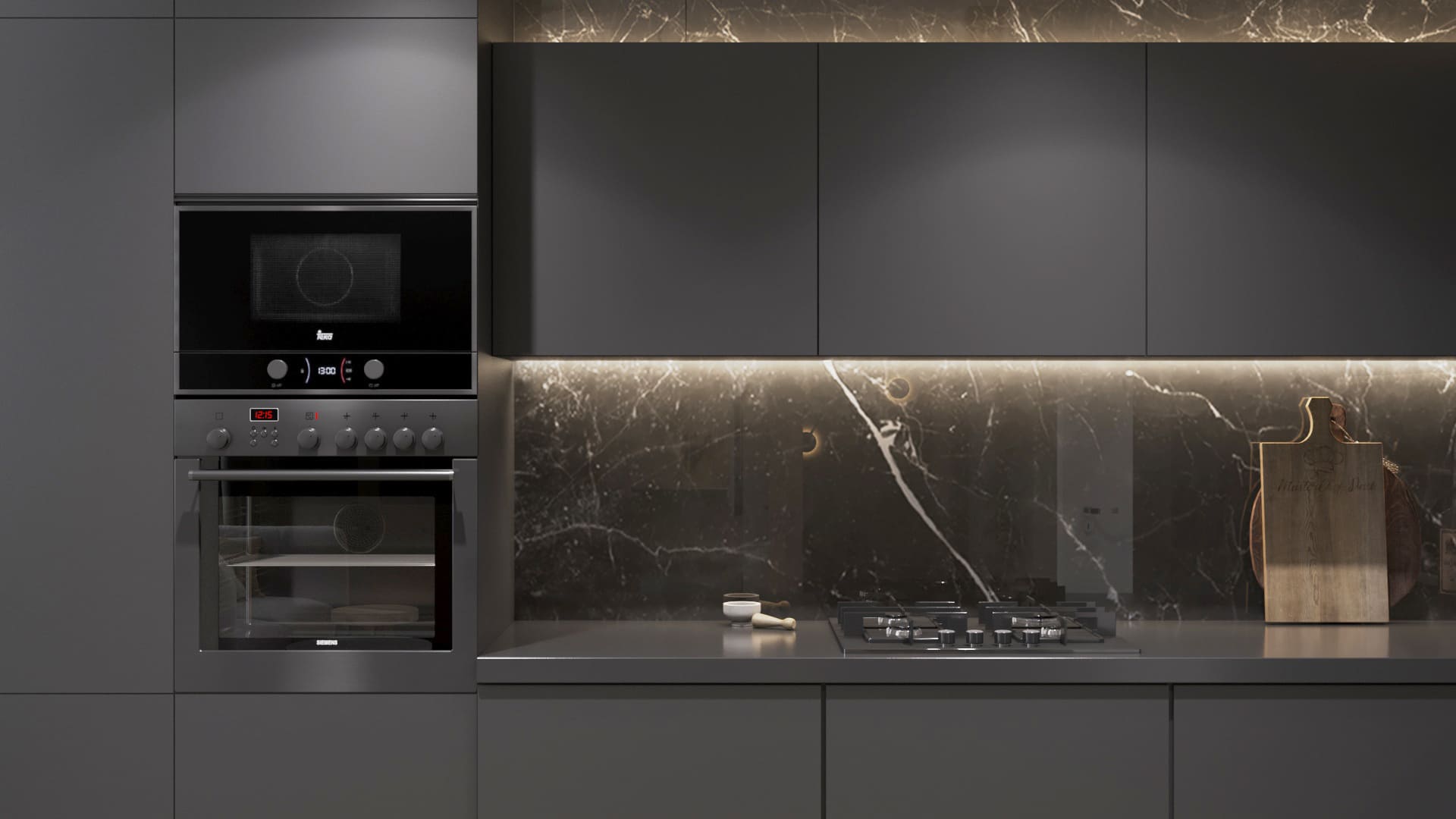

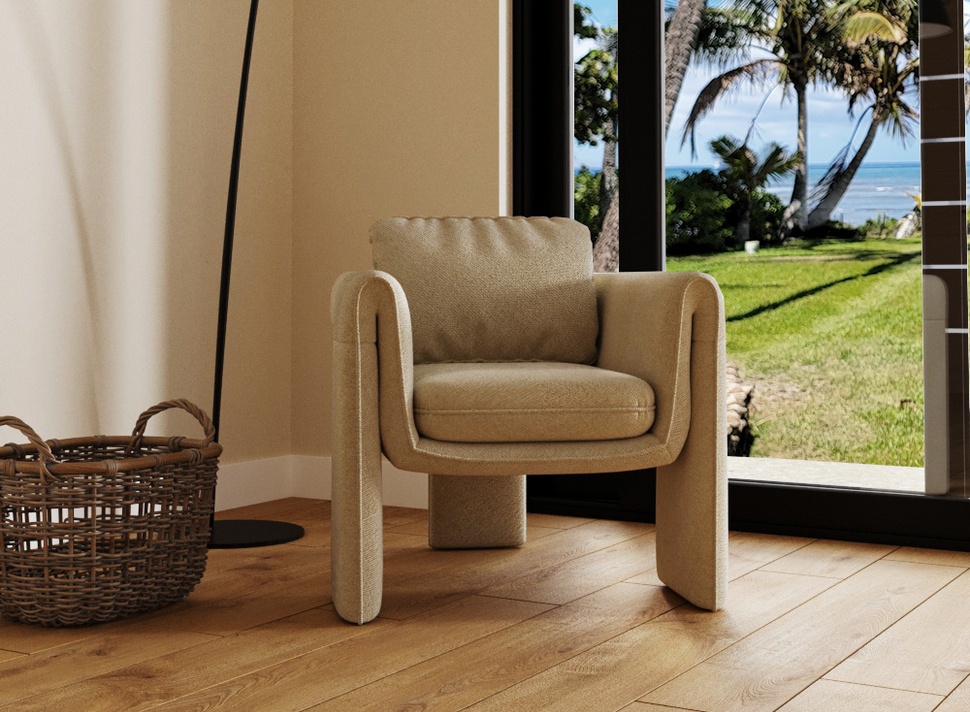
Image from Yousee Studio
One notable case study in architectural visualization is the work done for the Louvre Abu Dhabi, where detailed 3D renders were used to present the intricate design of the museum's dome, which consists of nearly 8,000 unique metal stars arranged in a complex geometric pattern. The renders clearly understood how the dome would filter light into the museum, creating a 'rain of light' effect, which was pivotal in conveying the architectural intent and the space's ambiance.
These real-world applications underscore the transformative impact of mastering detail in 3D product rendering. By achieving high realism, companies and professionals can improve the design process, enhance marketing materials, and ultimately drive engagement and sales. As technology advances, the possibilities for detailed 3D rendering will expand, opening new avenues for innovation and creativity across industries.
Future Trends in 3D Product Rendering
As we peer into the horizon of 3D product rendering, several emerging trends and technologies promise to elevate the level of detail and realism in digital visualizations. One of the most exciting developments is the integration of AI and machine learning into rendering software. AI algorithms are increasingly used to automate and enhance the rendering process, from optimizing render times to generating photorealistic textures. For instance, NVIDIA's Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) uses AI to increase the resolution of rendered images without additional computational power, delivering crisp, high-quality images at a fraction of the traditional rendering time.
Another trend poised to redefine the landscape of 3D rendering is the advent of real-time rendering technologies. Engines like Unreal Engine and Unity, traditionally used in the gaming industry, are now being adopted for product visualization, architectural walkthroughs, and interactive marketing experiences. Real-time rendering allows instant visualization of changes, enabling a more iterative and dynamic design process. This immediacy streamlines workflow and enables immersive experiences such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), which are becoming increasingly prevalent in showcasing products and designs in context.
Converging 3D rendering with VR and AR technologies opens new frontiers for product interaction and customer engagement. Virtual showrooms, for example, allow customers to explore a range of products in a fully immersive 3D environment, interacting with them in ways not possible in the physical world. Conversely, AR applications enable consumers to visualize products in their space before purchasing, enhancing confidence and satisfaction. As these technologies become more accessible, their integration into 3D Product rendering workflows will become standard practice, further blurring the lines between digital and physical realities.
Sustainability and environmental consciousness are also influencing the future of 3D rendering. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, the ability to create detailed digital prototypes and visualizations reduces the need for physical samples and mock-ups, minimizing waste and resource consumption. This eco-friendly aspect of 3D rendering is particularly relevant in the context of global sustainability goals, making it a tool for enhancing detail and realism and promoting responsible design and manufacturing practices.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Ray Lisbon is a content writer and the author of this article.