Turning Ideas into Reality: The Art of 3D Product Modeling
In the realm of product development, the role of a 3D product modeling company has become indispensable, transforming mere ideas into tangible realities. This article delves into the sophisticated art of 3D product modeling, uncovering the techniques and technologies that enable designers to create, iterate, and perfect their visions with unprecedented precision and efficiency. By exploring the core methodologies and tools that power 3D Modeling, we'll shed light on how this digital craft is reshaping the landscape of product design, making it possible to bring even the most complex and innovative ideas to life.
Introduction to 3D Product Modeling
3D product modeling has revolutionized the design process, offering a digital canvas to explore and refine ideas in a virtual environment. This transformative approach enables designers to visualize products in three dimensions, far surpassing the limitations of traditional 2D sketches. The essence of 3D Modeling lies in its ability to provide a detailed and accurate representation of products, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of aesthetics, functionality, and ergonomics before any physical prototype is constructed.
This shift towards digital Modeling has been propelled by the demand for faster development cycles and the need to innovate continually in a competitive market. 3D product modeling companies are at the forefront of this shift, employing advanced software and techniques to create models that are not only visually stunning but also precisely aligned with engineering requirements. The ability to iterate designs quickly, test different scenarios, and visualize products in real-world contexts has significantly shortened development timelines and enhanced the final product's quality.
Core Techniques in 3D Product Modeling
Several core techniques underpin the art of 3D product modeling, each suited to different aspects of the design process. Solid Modeling is one of the fundamental techniques widely used for its precision and ability to create models defined by exact geometrical parameters. This technique is indispensable in industries where structural integrity and tight tolerances are critical, such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. Solid models are fully defined, volumetric representations, making them ideal for engineering analysis and simulation, ensuring that the product looks right and performs as intended under various conditions.
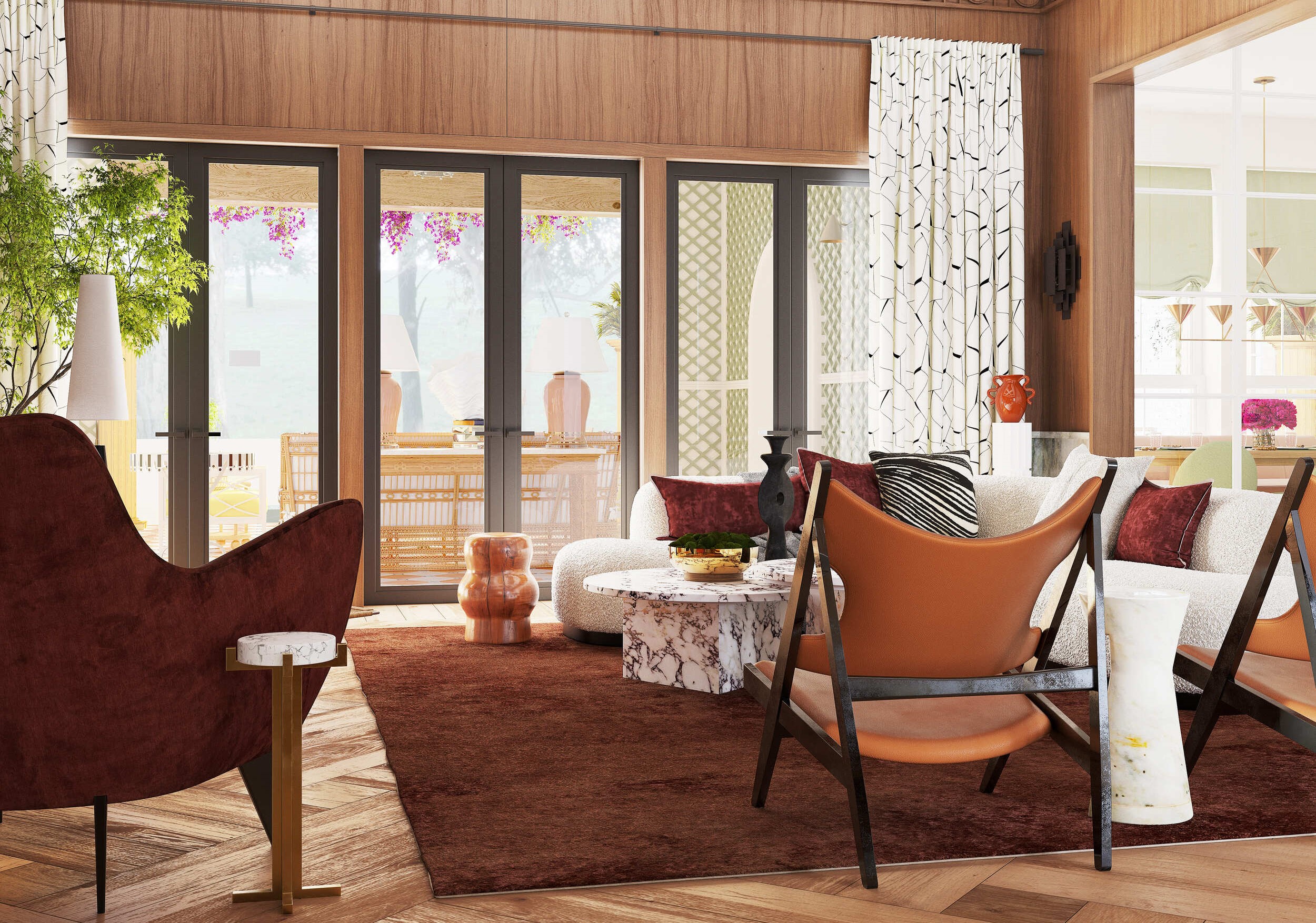

Image from Yousee Studio
Surface modeling, on the other hand, offers a more flexible approach, ideal for designing complex, freeform shapes often seen in consumer electronics, household appliances, and automotive exteriors. This technique defines the product's external surfaces, allowing designers to manipulate curves and shapes to achieve the desired aesthetic appeal. Surface modeling is particularly valued in the early conceptual stages of design, where visual appeal and brand identity play a significant role in product differentiation.
Each modeling technique brings its own set of advantages, and the choice between them often depends on the project's specific requirements. In many cases, designers employ these techniques, using solid Modeling for the core structural components and surface modeling for the external aesthetic elements. This hybrid approach ensures that the final product is functional, manufacturable, visually appealing, and aligned with the brand's identity.
Technological Tools Powering 3D Modeling
The leap from conceptual sketches to detailed 3D models is facilitated by various technological tools that have become indispensable in the product design industry. At the forefront of these tools is a suite of 3D modeling software, each offering unique features and capabilities tailored to different aspects of the modeling process. Autodesk's AutoCAD is renowned for its precision and versatility, making it a staple in industries that require exacting detail, such as architecture and engineering. Blender, known for its open-source nature, provides a comprehensive toolset for Modeling, rendering, and animation, making it a popular choice among independent designers and small studios.
SolidWorks stands out for its parametric modeling capabilities, allowing designers to build complex models based on geometric and dimensional constraints, making it ideal for mechanical and industrial design applications. Meanwhile, Autodesk Maya and 3ds Max offer robust tools for creating highly detailed models and realistic animations, catering to the entertainment, film, and game development industries.
Integrating advanced features such as real-time rendering, physics-based simulations, and AI-assisted design automation marks the evolution of these software tools. Real-time rendering technologies, such as those powered by Unreal Engine and Unity, enable designers to visualize their models in lifelike scenarios, adjusting materials, lighting, and environmental settings on the fly. This capability significantly enhances the iterative design process, allowing for rapid prototyping and testing of design concepts.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies have also become integral to 3D Modeling, offering immersive platforms for showcasing and interacting with 3D models. AR applications enable designers to project virtual prototypes into real-world environments, providing a tangible sense of scale, context, and usability. VR takes this immersion further, allowing designers and stakeholders to enter fully realized 3D environments, interact with models, and assess design choices in a virtual space.
Benefits of 3D Product Modeling for Designers and Businesses
Adopting 3D product modeling brings many benefits to both designers and businesses, fundamentally transforming the product development lifecycle. One of the most significant advantages is the enhanced visualization it provides. Designers can create lifelike representations of products, complete with detailed textures, materials, and lighting, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of the design's aesthetic and functional aspects. This level of detail facilitates better decision-making, ensuring that the final product aligns with the envisioned design and meets customer expectations.
For businesses, 3D product modeling offers cost savings and efficiency gains throughout product development. By identifying and resolving design issues in the virtual model, companies can avoid costly revisions and material waste during physical prototyping and manufacturing stages. This reduces development costs and accelerates time-to-market, providing a competitive advantage in fast-paced industries.

Image from Yousee Studio
Moreover, 3D Modeling enhances collaboration and communication among project teams and stakeholders. Digital models can be easily shared, reviewed, and modified, bridging the gap between designers, engineers, and decision-makers. This collaborative approach fosters a more integrated and agile development process, where feedback can be quickly incorporated, and design iterations can be efficiently managed.
Additionally, 3D product models are invaluable for marketing and customer engagement strategies. Businesses can use these models in promotional materials, interactive websites, and AR/VR applications, providing customers with an engaging and informative product exploration experience. This boosts marketing efforts and empowers customers to make informed purchasing decisions, enhancing satisfaction and loyalty.
From Concept to Prototype: The 3D Modeling Workflow
The journey from an initial concept to a physical prototype is intricate and fascinating, involving a series of well-defined steps that leverage the full potential of 3D modeling technologies. The workflow begins with the conceptualization phase, where ideas are brainstormed and preliminary sketches are drawn. This creative process sets the foundation for the product, outlining its purpose, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
Transitioning from sketches to digital models marks the beginning of the 3D modeling phase. Designers use advanced software to construct the product in a virtual environment, meticulously shaping each curve, edge, and surface to match the envisioned design. This stage is where the core techniques of solid, surface, and wireframe modeling are applied, each serving a unique purpose in realizing different aspects of the product. Solid Modeling lays the groundwork for the product's functional components, surface modeling brings the aesthetic elements to life, and wireframe modeling provides a skeletal framework that guides the overall structure.
The refinement and testing phase ensues after the creation of the 3D model. Designers scrutinize the model for inconsistencies, ensuring every detail aligns with the design specifications and functional requirements. Virtual simulations and analyses, such as stress tests and aerodynamics, are conducted to predict how the product will perform under various conditions, allowing designers to make necessary adjustments and optimizations.
The culmination of the 3D modeling workflow is the prototyping phase. With the digital model finalized, rapid prototyping techniques such as 3D printing are employed to create physical product prototypes. These prototypes are tangible representations that can be evaluated for ergonomics, usability, and overall design integrity. Feedback gathered during this stage can lead to further iterations in the 3D model, refining the product until it meets all desired criteria.
Best Practices for a Seamless 3D Modeling Workflow
Several best practices should be adhered to to ensure a smooth and efficient 3D modeling workflow. Continuous collaboration among designers, engineers, and stakeholders is crucial throughout the process, fostering an environment where feedback is actively sought and incorporated. Utilizing cloud-based platforms for 3D modeling projects enhances collaboration, enabling real-time updates and access to the latest versions of the model.
Maintaining a flexible and iterative approach is also essential. The ability to quickly adapt and iterate on designs in response to new insights or challenges is one of the critical advantages of 3D Modeling. Embracing this flexibility ensures that the final product is innovative and thoroughly vetted for market readiness.
Furthermore, staying abreast of the latest technological advancements in 3D modeling software and hardware can significantly impact the workflow's efficiency and outcomes. Investing in ongoing training and development ensures that design teams can leverage their projects' most cutting-edge tools and techniques.

Image from Yousee Studio
In conclusion, the art of 3D product modeling represents a pivotal shift in how products are designed, developed, and brought to market. By embracing the advanced techniques and technologies that underpin this discipline, designers, and businesses can turn their most ambitious ideas into reality, transcending traditional limitations to innovate and create with unprecedented freedom and precision. The 3D modeling workflow, from concept to prototype, embodies a meticulous yet creative process that exemplifies the convergence of art, science, and technology in modern product design. As we look to the future, the continued evolution of 3D Modeling promises to expand the horizons of what's possible further, driving forward the creation of products that are not just functional and aesthetically pleasing but genuinely revolutionary.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Ray Lisbon is a content writer and the author of this article.