From Concept to Creation: The Journey of 3D Product Modeling
Introduction to 3D Product Modeling
The advent of 3D modeling technologies has profoundly transformed product design and manufacturing. The ability to create 3D product models has streamlined the design process and opened up new avenues for creativity and innovation. This transformation allows designers and engineers to convert their visions into detailed, manipulable digital formats, significantly enhancing the precision and efficiency of product development.
3D product modeling bridges conceptual ideas and tangible creations, enabling professionals to visualize, analyze, and refine products in a virtual environment before committing to costly production processes. This capability is crucial in today's fast-paced market, where speed and accuracy are paramount. The use of specialized software such as Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, or SolidWorks facilitates the creation of highly detailed and accurate models that can be used for a wide range of applications, from prototyping and functional testing to marketing and sales.
 |
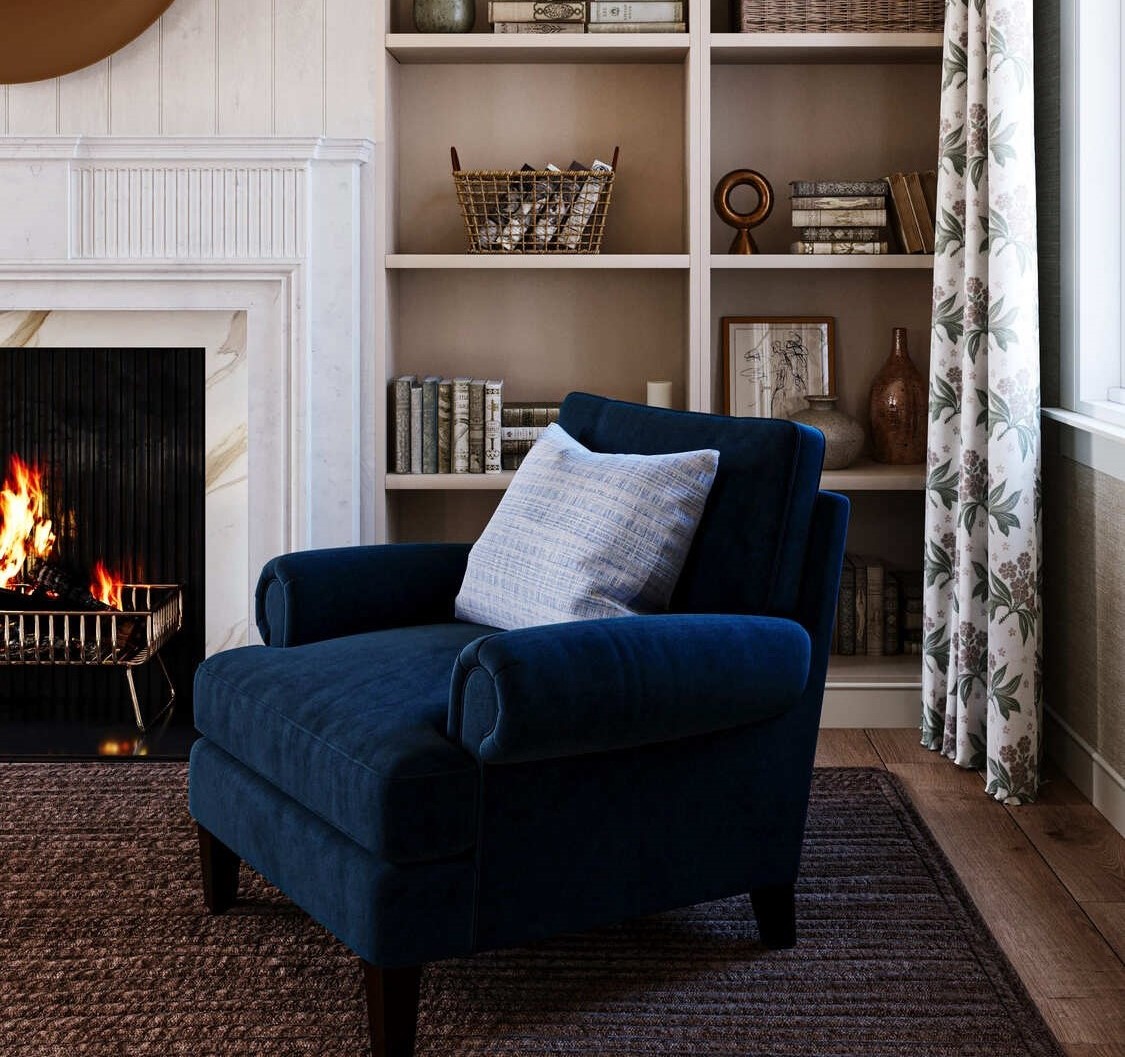 |
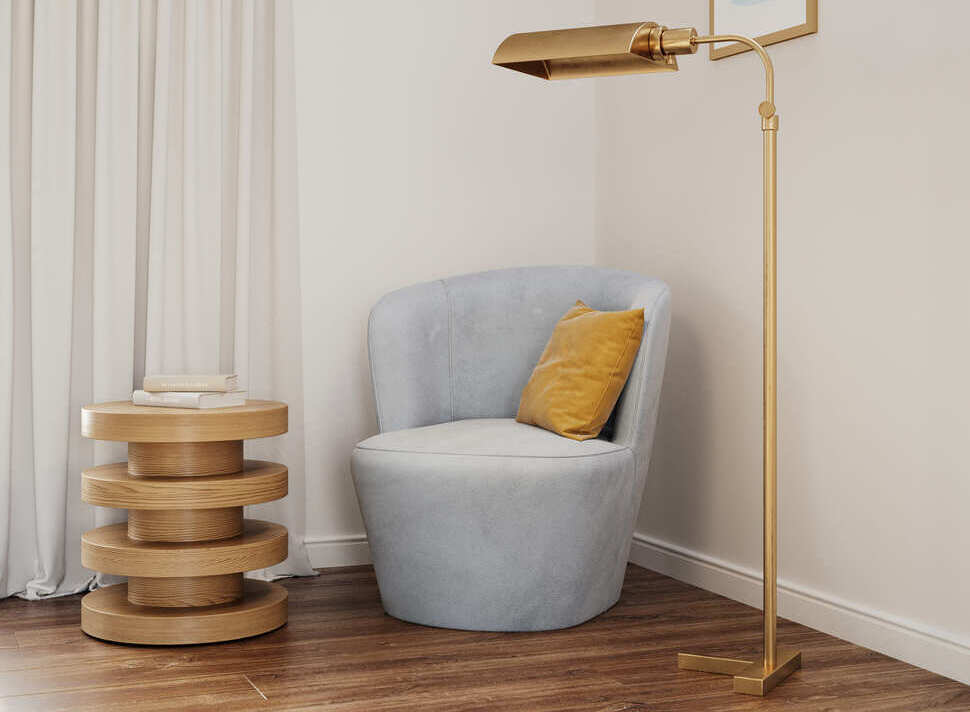
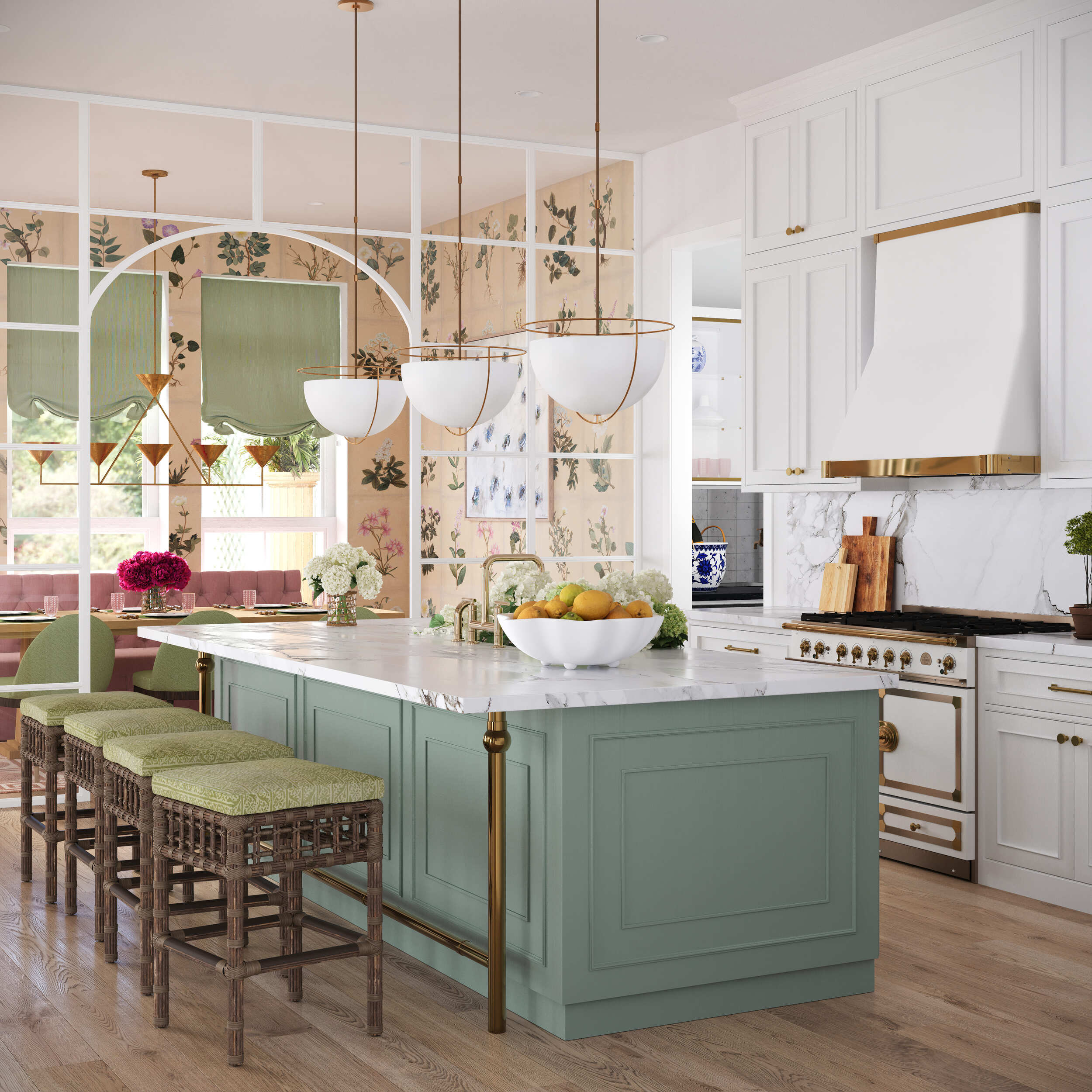
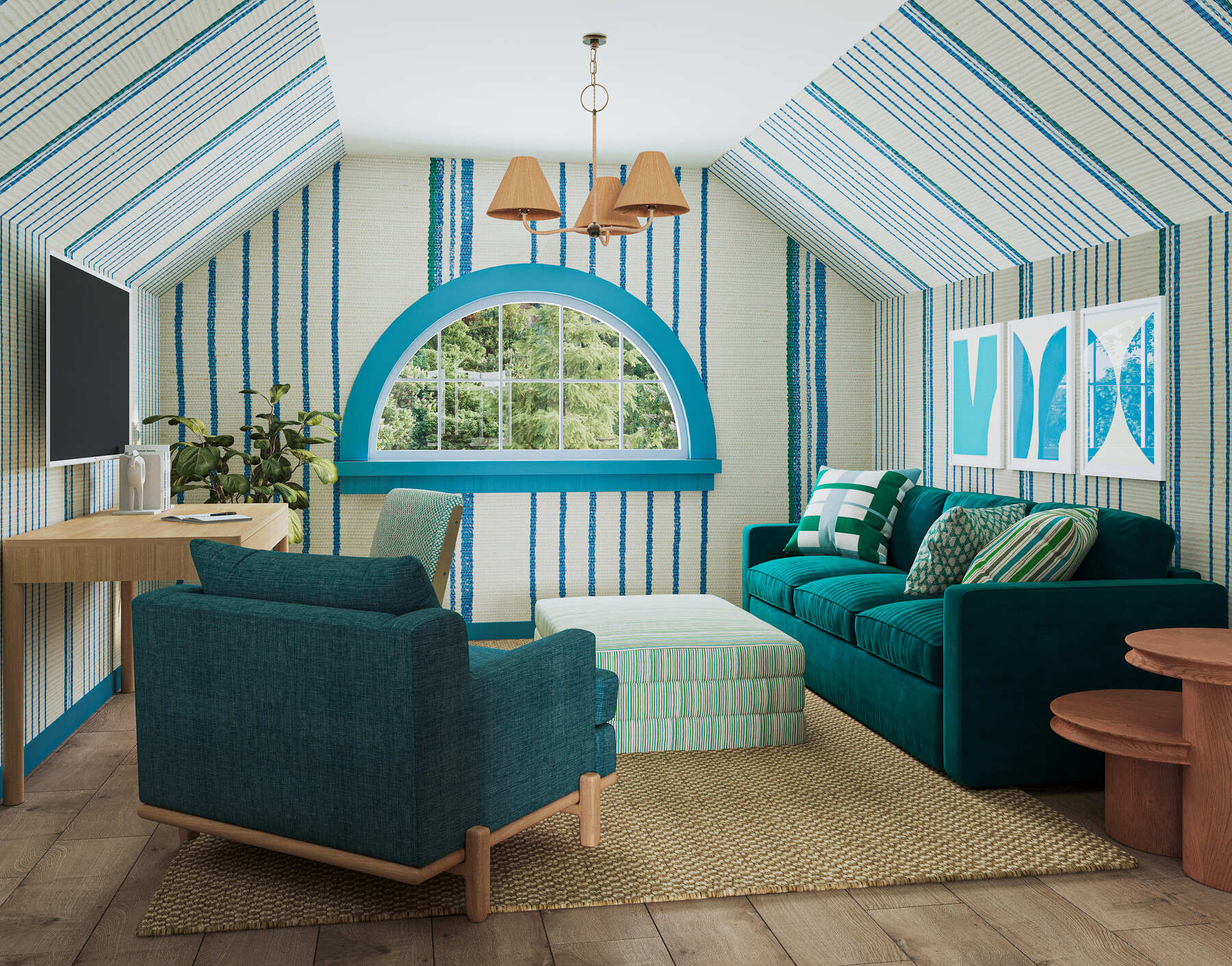
Image from Yousee Studio
The significance of 3D Modeling in modern product presentation cannot be overstated. It allows for exploring design alternatives, stress and strain analysis, and the simulation of real-world usage without the need for physical prototypes. Moreover, 3D Modeling enables the creation of stunning visuals for marketing purposes, allowing customers to engage with products in an immersive and interactive manner. This introductory exploration sets the stage for a deeper dive into the journey of 3D product modeling, from the initial concept to the final creation.
The Conceptualization Phase
Gathering Ideas and Requirements
The journey of 3D product modeling begins with the conceptualization phase, where the initial groundwork for the project is laid. This stage involves extensive collaboration between designers, engineers, and stakeholders to gather ideas, define project requirements, and establish clear objectives for the product. It's a critical process that involves brainstorming sessions, market research, and feasibility studies to ensure that the product concept is viable, innovative, and meets the target audience's needs.
Sketching is pivotal during this phase as a primary tool for visualizing and communicating ideas. These preliminary sketches provide a visual reference that guides the 3D modeling process, offering a flexible and efficient way to explore different design concepts and adjust based on feedback. The ability to quickly iterate on designs at this early stage is invaluable, saving time and resources by identifying potential issues before the modeling process begins.
Client-Designer Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration between the client and the design team are essential for refining the product concept. This collaborative effort ensures that the final product aligns with the client's vision and expectations. Technology advancements have facilitated this process, allowing for real-time collaboration and feedback through digital platforms. Designers can share digital sketches and concept art with clients and stakeholders, enabling immediate input and adjustments.
This phase defines the product's aesthetic aspects, as well as its functionality, usability, and manufacturability. Decisions made during the conceptualization phase profoundly impact the subsequent stages of the design process, influencing everything from the choice of materials to the complexity of the manufacturing process. A well-defined concept serves as a blueprint for the 3D modeling phase, ensuring the design team has a clear direction and a solid foundation.
In conclusion, the conceptualization phase is a critical step in the journey of 3D product modeling, setting the stage for successful product development. It's a phase where creativity meets practicality and where the initial vision begins to take shape. The collaboration between clients and designers during this stage is pivotal, ensuring that the final product meets and exceeds expectations. As we move forward in the journey of 3D product modeling, the importance of a well-executed conceptualization phase becomes increasingly apparent, laying the groundwork for the innovative and efficient creation of products.
Design and Development in 3D Modeling
Creating Detailed 3D Models
The transition from conceptual sketches to detailed 3D models marks a significant step in the product development process. This phase involves using advanced 3D modeling software to create precise digital representations of the product. Designers and engineers work closely to ensure that every aspect of the model meets the specified requirements, including dimensions, functionality, and aesthetics. The choice of software is crucial at this stage, with industry standards like Autodesk's AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Rhino being preferred for their robust features and precision.
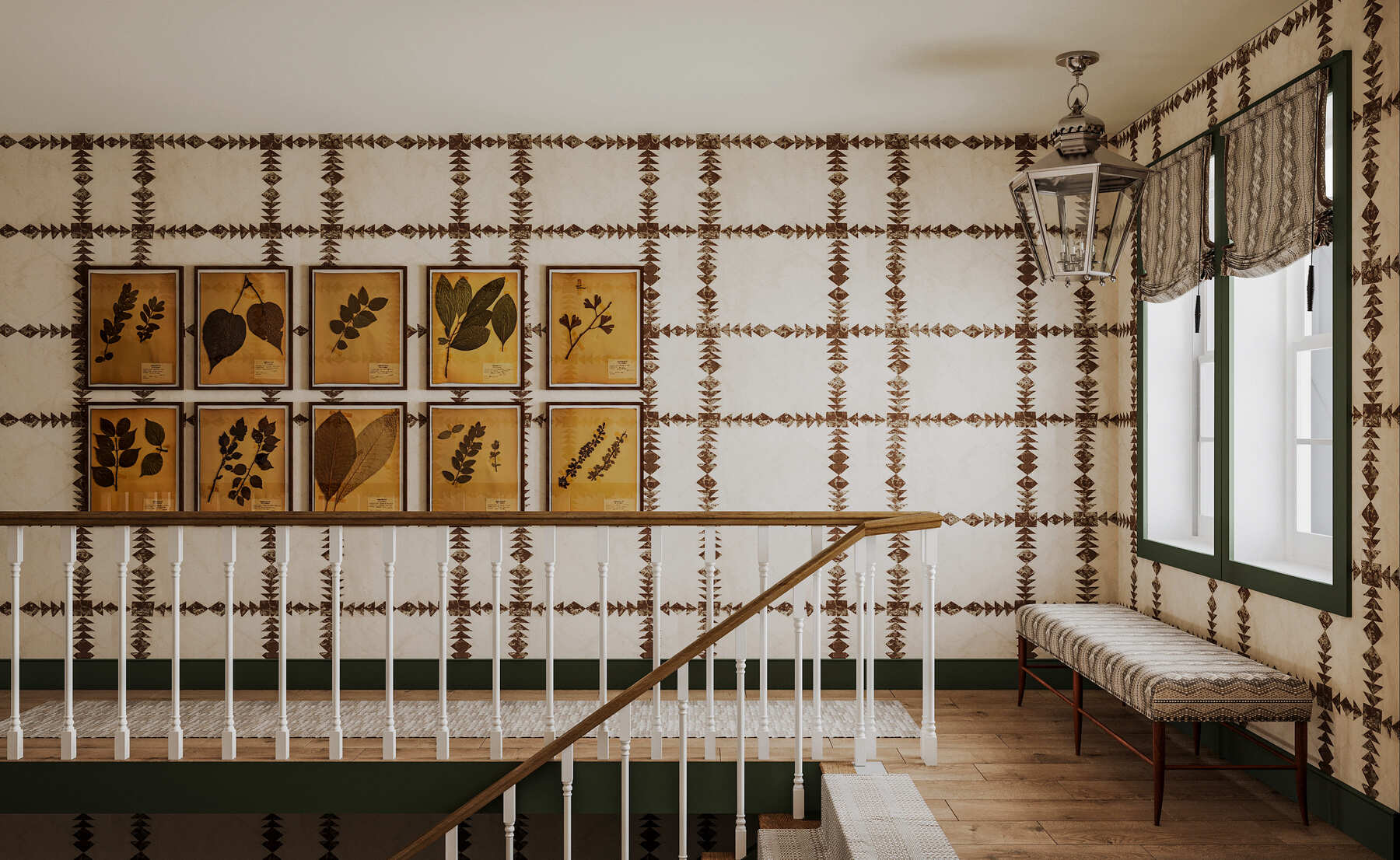

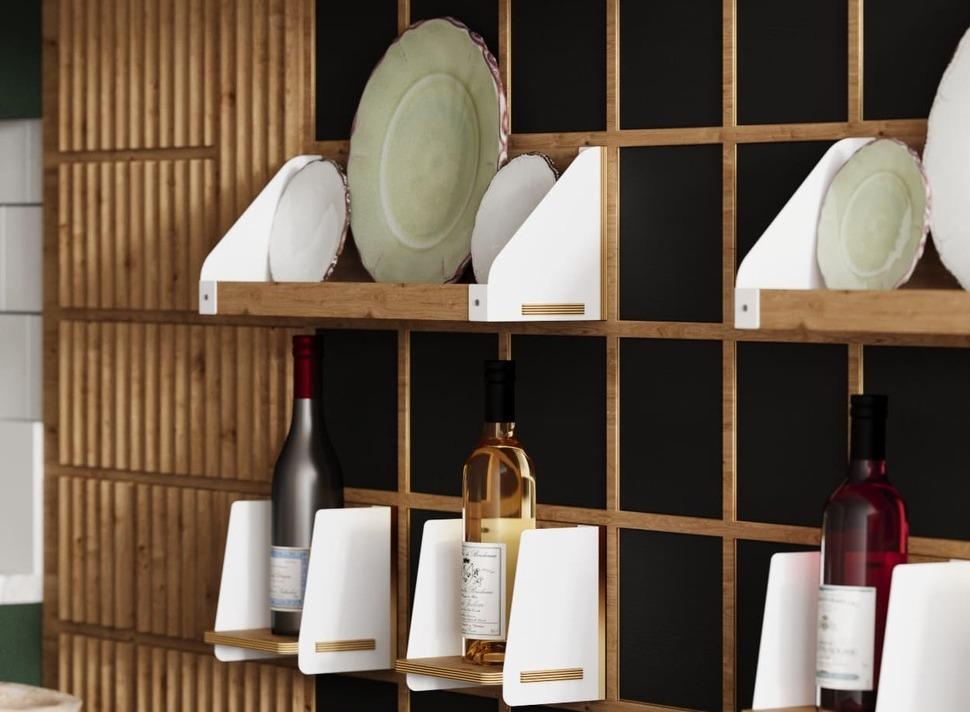
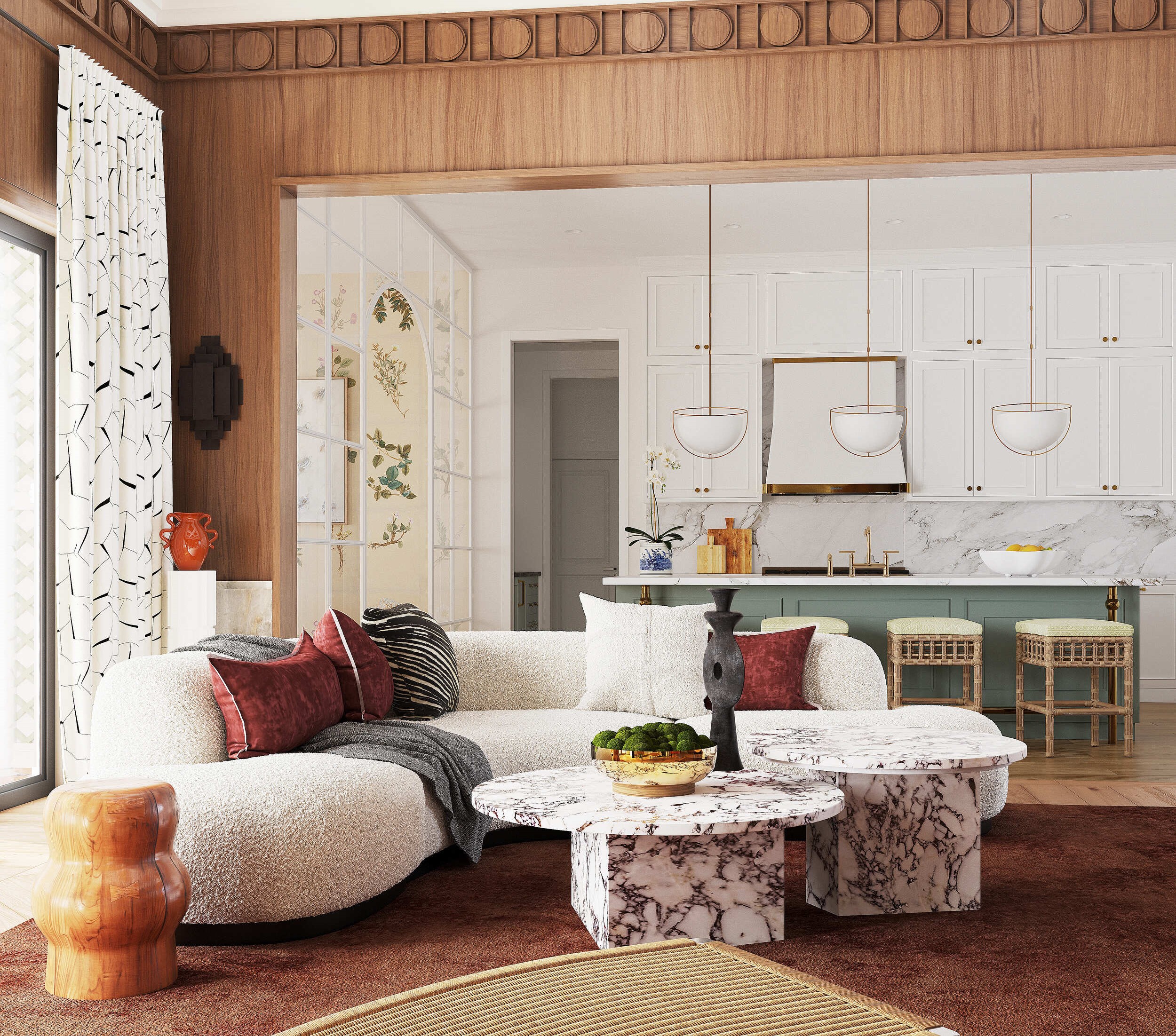
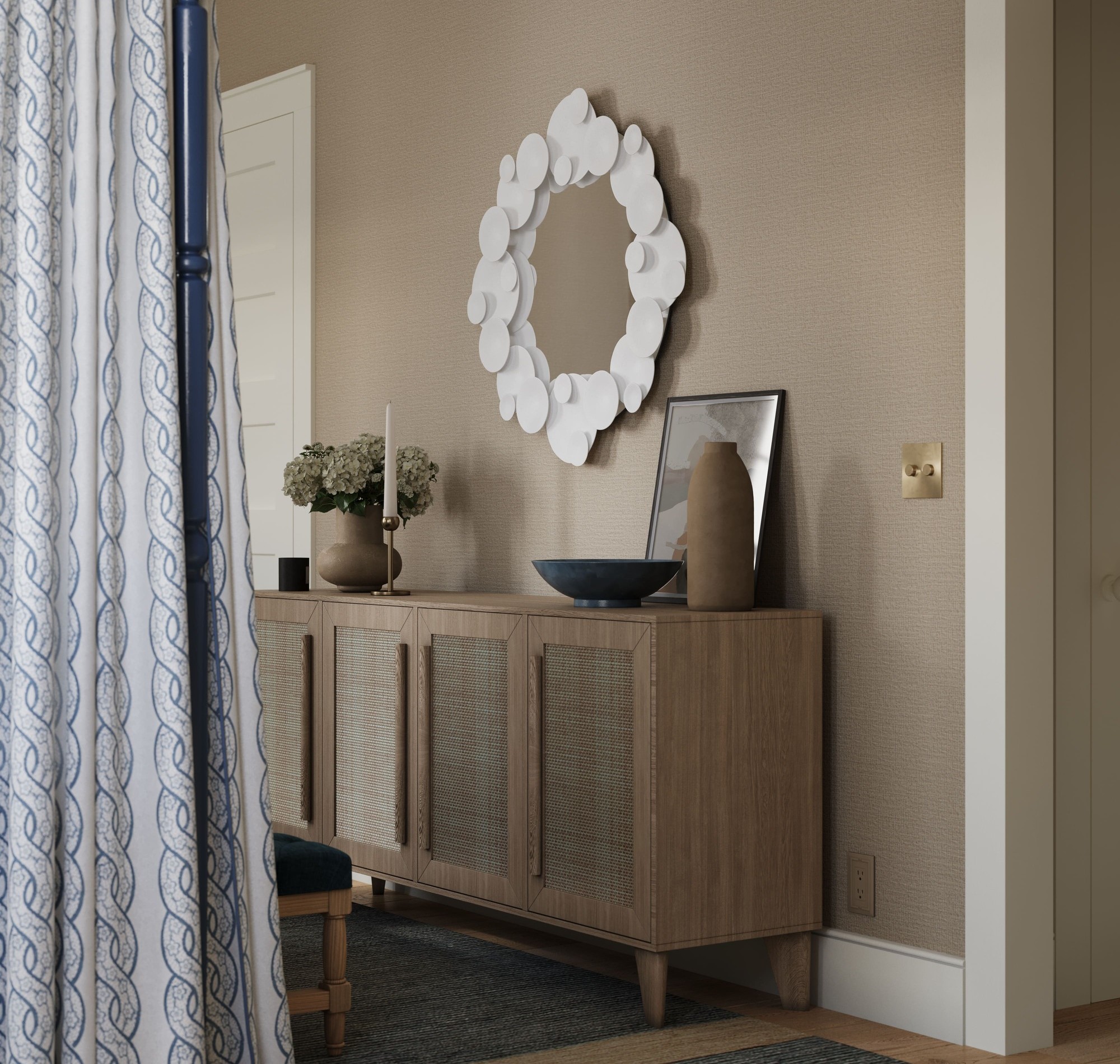
Image from Yousee Studio
Creating a 3D model is a meticulous process that requires a deep understanding of the product's design and the software's capabilities. Designers must consider the product's physical properties, such as weight distribution, material flexibility, and stress points, to create a model that is visually accurate and functionally viable. This digital model serves as the foundation for all subsequent stages of Development, allowing for simulations and analyses that can predict how the product will perform in real-world conditions.
Incorporating Textures, Colors, and Materials
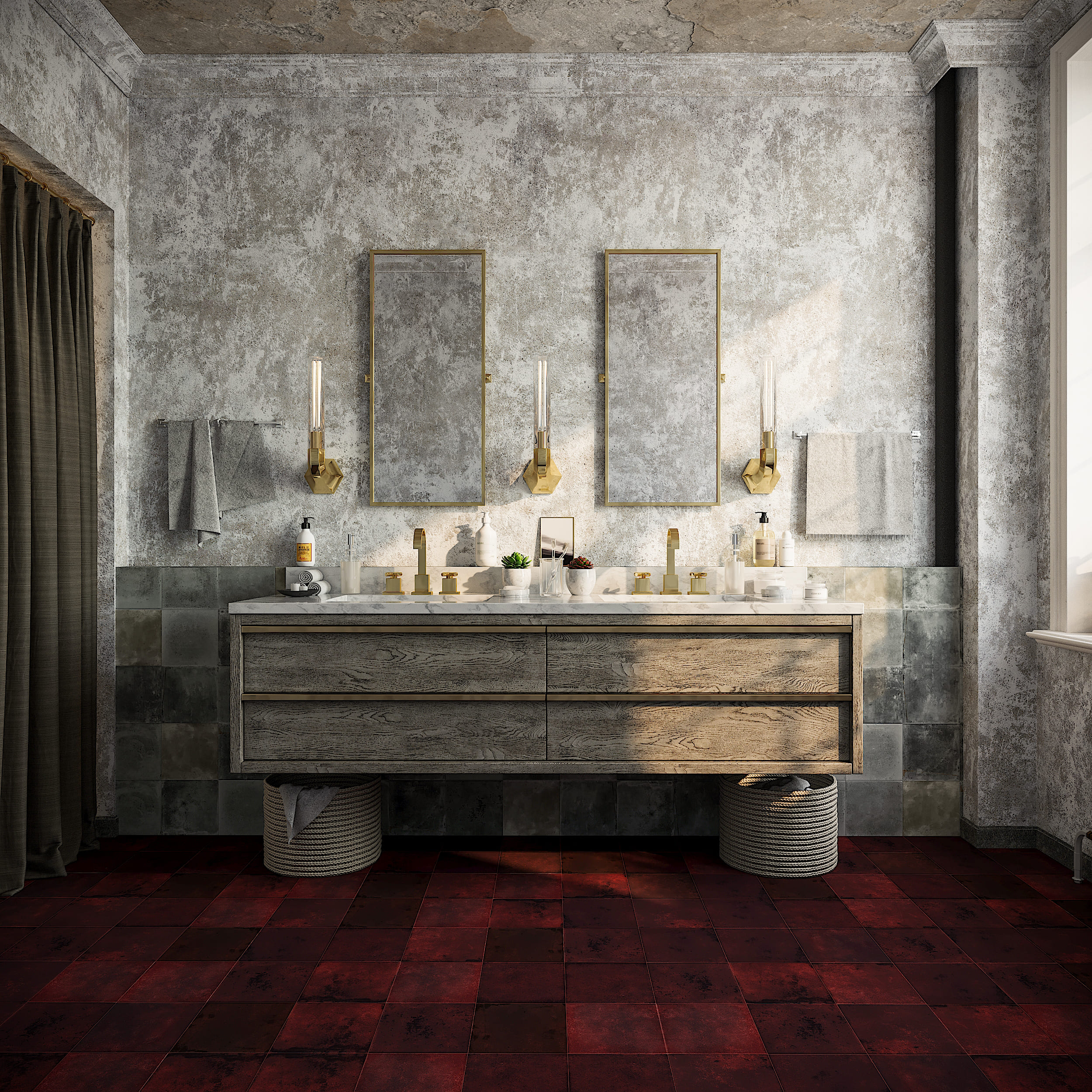
Beyond the basic shape and structure, applying textures, colors, and materials is essential for bringing the 3D model to life. This step is crucial for products where aesthetic appeal is a crucial selling point. Modern 3D modeling software offers a wide range of tools and libraries that allow designers to apply realistic textures and finishes to their models, from the gloss of polished metal to the grain of natural wood.
This level of detail is beneficial for visualizing the final product and marketing and promotional purposes. High-quality renders of the 3D model can be used in brochures, websites, and advertisements, providing potential customers with a realistic preview of the product. Furthermore, experimenting with different colors and materials in the digital space enables designers to explore various design options without needing physical samples, saving time and resources.
Prototyping and Testing
From Digital to Physical: Creating Prototypes
Once the 3D model has been finalized, the next step in the product development process is to create a physical prototype. This stage is critical for evaluating the design's practicality and identifying potential issues that may not have been apparent in the digital model. Rapid prototyping technologies, such as 3D printing, have revolutionized this process, allowing for quick and cost-effective production of prototypes directly from the 3D model.
3D printing, in particular, offers unparalleled flexibility in prototyping, enabling the creation of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This technology allows designers and engineers to hold a tangible version of their product in their hands, test its functionality, and gather feedback from stakeholders and potential users. The insights gained from this physical testing are invaluable for refining the product design, ensuring that the final product meets all requirements and expectations.
Iterative Testing and Refinement
The prototyping and testing phase is inherently iterative, with each prototype as a learning tool for further improvement. Multiple rounds of prototyping and testing are not uncommon, especially for complex or innovative products. Each iteration brings the product closer to its final form, addressing ergonomics, durability, and user experience.
In addition to physical testing, virtual simulations can be crucial in this phase. Advanced software tools enable engineers to conduct stress tests, fluid dynamics analyses, and other simulations to predict how the product will perform under various conditions. These virtual tests can identify potential problems before they arise in physical prototypes, further streamlining the development process.
The design and development phase, followed by prototyping and testing, are critical stages in the journey of 3D product modeling. These steps transform initial concepts into tangible products, ready for finalization and production. The meticulous attention to detail required at each stage ensures that the final product is aesthetically pleasing but also functional, durable, and user-friendly. As technology continues to advance, the possibilities for innovation in 3D product modeling and prototyping expand, offering exciting opportunities for designers and manufacturers to bring their most ambitious ideas to life.
Finalizing and Production
Final Adjustments and Pre-Production
After rigorous prototyping and testing, the 3D product model enters the finalization stage, where the last adjustments are made before the product goes into production. This crucial phase involves refining the design based on feedback from testing, ensuring that the product meets the desired specifications and adheres to manufacturing constraints and industry standards. It's a collaborative effort between designers, engineers, and manufacturing teams to ensure that the digital model translates seamlessly into a manufacturable product.
Key considerations during this phase include the selection of materials for mass production, which may differ from those used in prototyping due to cost, availability, or manufacturing limitations. Additionally, designers might need to adjust the 3D model to accommodate manufacturing techniques or to optimize the product for assembly and packaging. This stage is also when final decisions on product aesthetics are made, solidifying choices regarding colors, finishes, and branding elements.
Streamlining the Manufacturing Process
The use of 3D models extends into the manufacturing process, where they serve as a detailed guide for production. Modern manufacturing technologies, such as CNC machining and 3D printing, can directly interpret these digital models, allowing for precise and efficient production. Integrating 3D models into the manufacturing workflow reduces the likelihood of errors and significantly speeds up the production time, as the need for manual interpretation of design drawings is minimized.
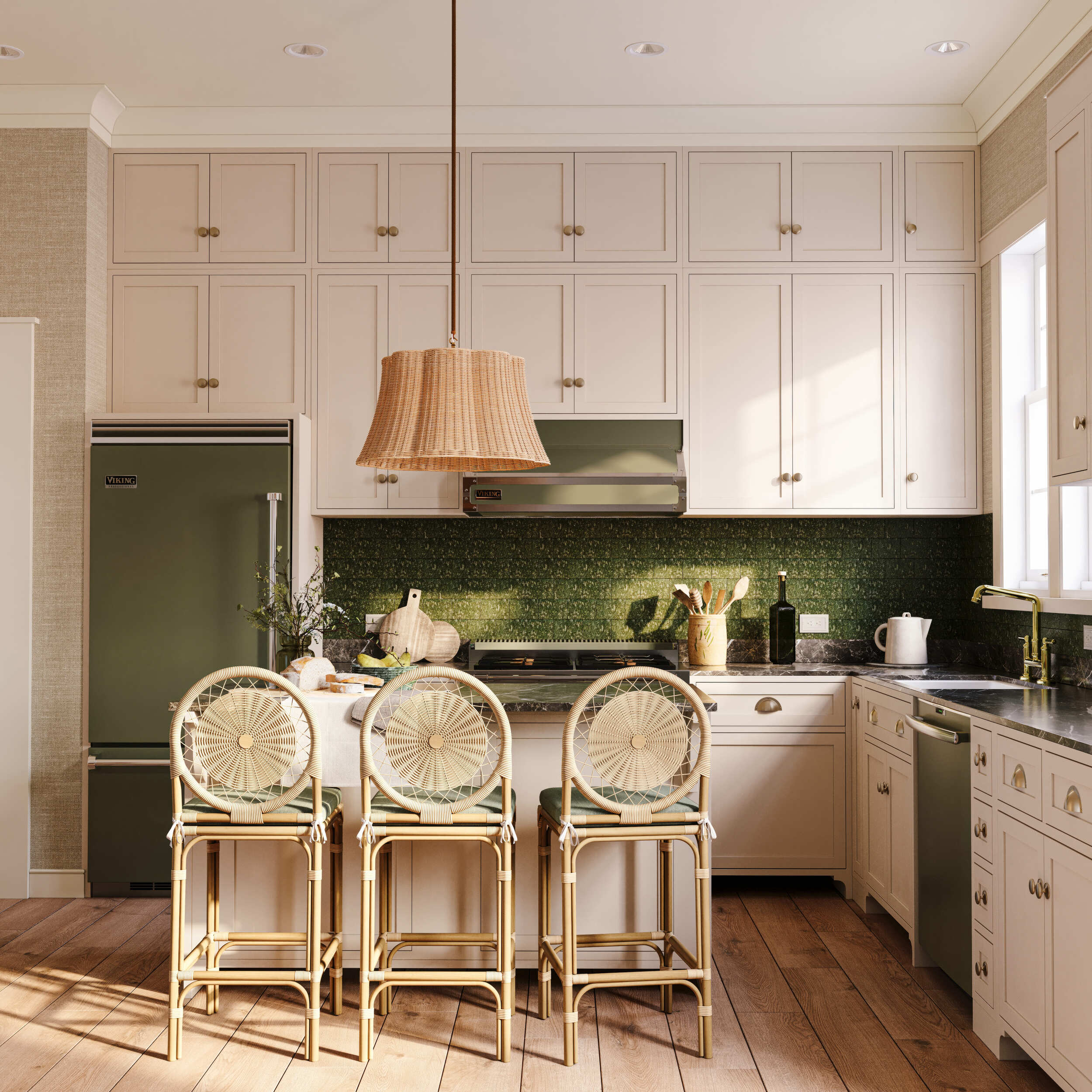 |
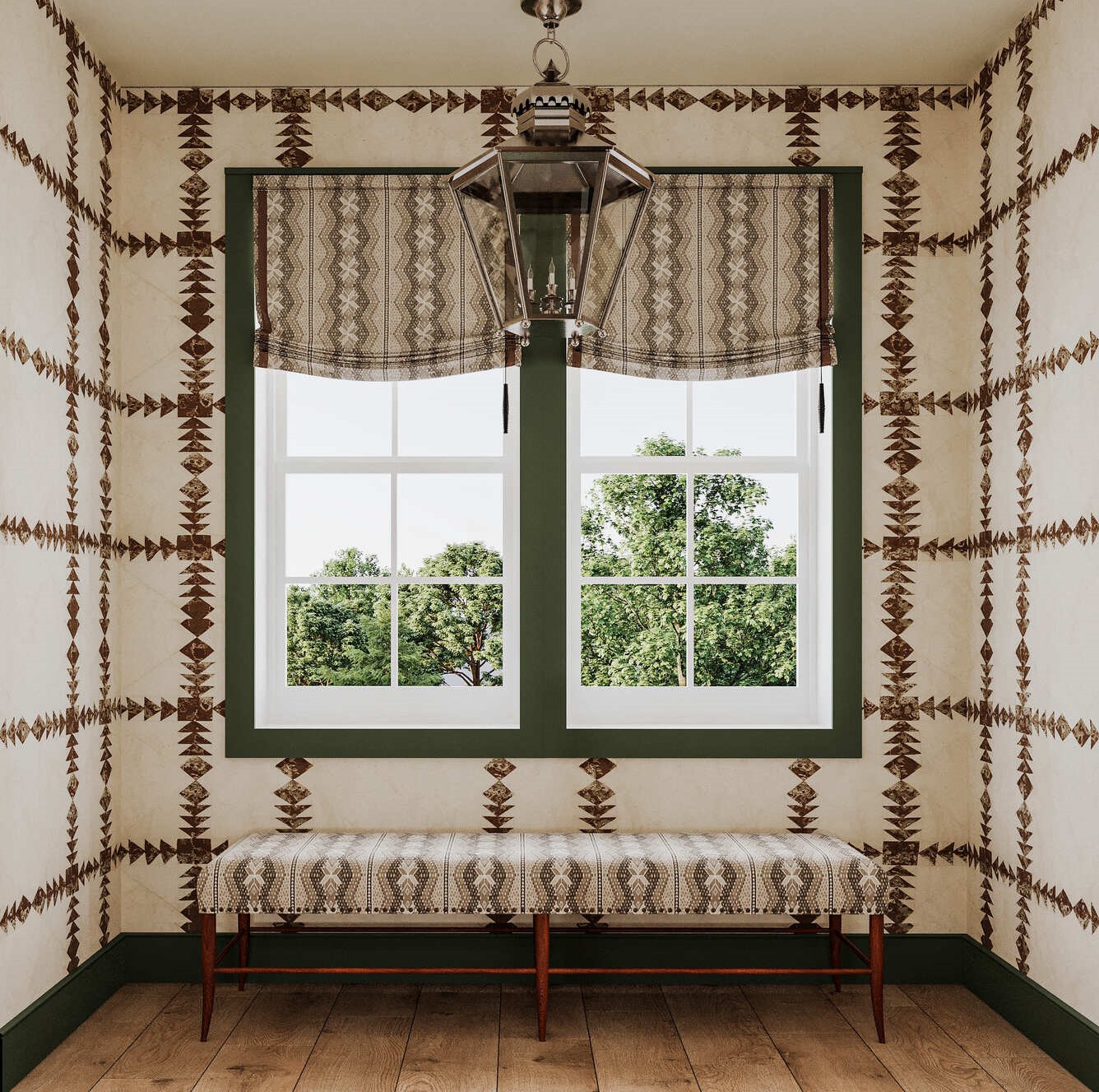 |
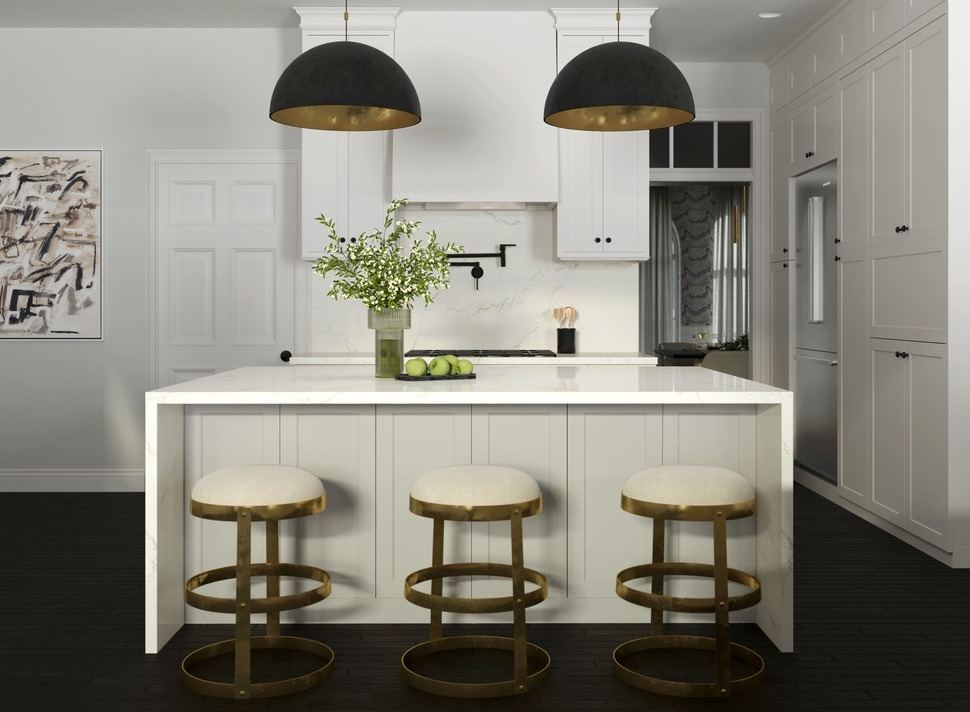
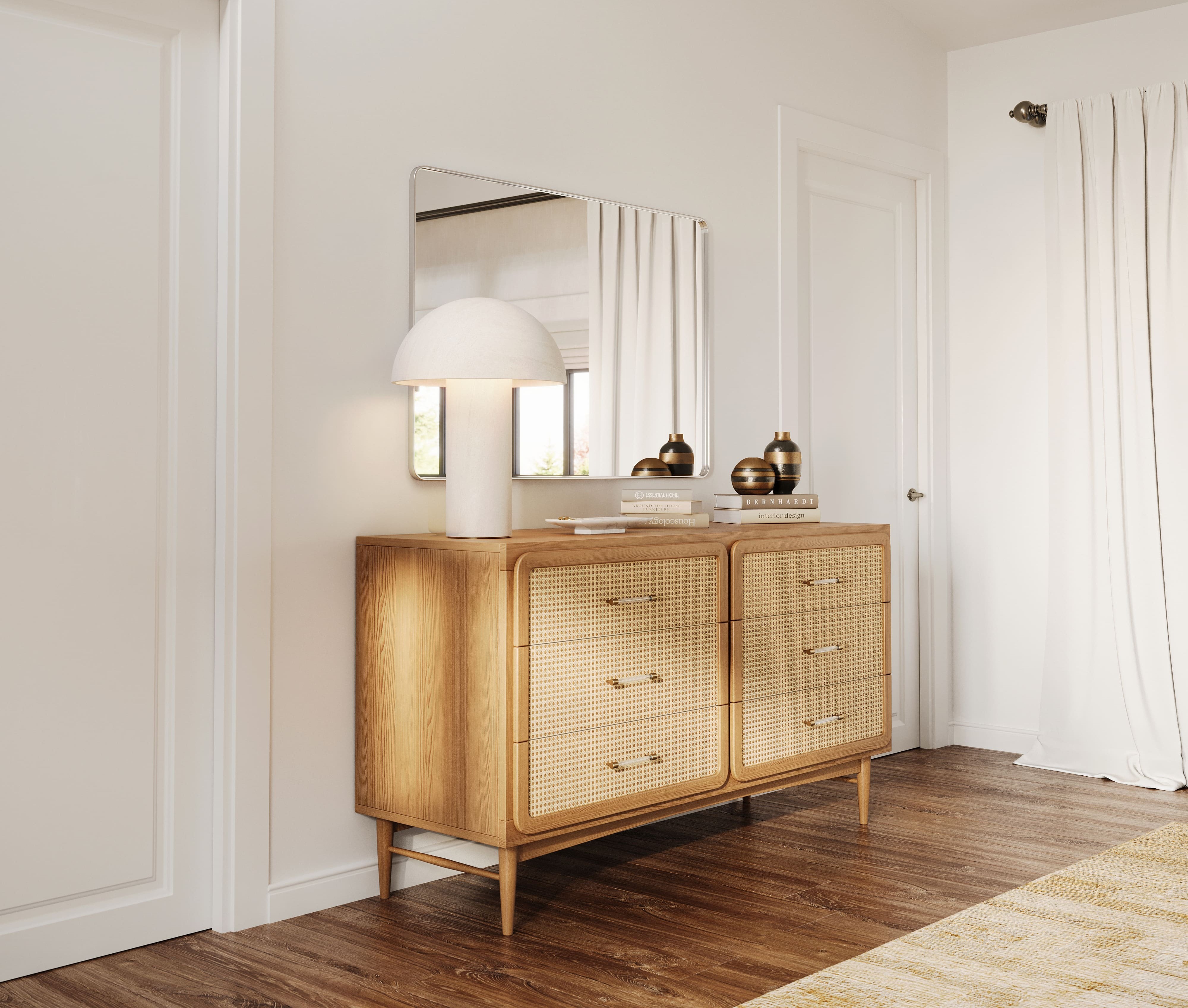
Image from Yousee Studio
Moreover, the digital nature of 3D models facilitates easy modifications and iterations, making it more straightforward to update the product design without extensive retooling or downtime in production. This flexibility is precious in today's market, where the ability to respond to consumer feedback or changes in demand quickly can provide a competitive edge.
Conclusion: Bridging Concepts with Reality
The journey from concept to creation through 3D product modeling is a testament to the transformative power of digital design and manufacturing technologies. By enabling designers to visualize and refine products in a virtual environment, 3D Modeling has streamlined the development process, reduced costs, and enhanced the quality and functionality of the final products. The iterative cycle of design, prototyping, testing, and finalization ensures that each product meets and exceeds the expectations of both manufacturers and consumers.
As we look to the future, the role of 3D Modeling in product development is set to grow even further, driven by advancements in software capabilities, prototyping technologies, and manufacturing techniques. The innovation potential is boundless, with 3D Modeling at the forefront of creating more innovative, sustainable, personalized products. The journey of 3D product modeling, from concept to creation, embodies the essence of modern engineering and design, turning imaginative ideas into tangible realities that enrich our lives.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Karen Spacey is a content writer and the author of this article.