Essential Apps for 3D Rendering and Visualization
In the ever-evolving digital design and visual communication landscape, 3D rendering and visualization have become indispensable tools for professionals across various industries. From architects and product designers to game developers and filmmakers, the ability to create lifelike, immersive digital environments has revolutionized how we conceptualize, present, and experience ideas. This article delves into the world of 3D rendering and visualization applications, exploring the cutting-edge software that's reshaping the industry and empowering creators to push the boundaries of visual storytelling.
The Evolution of 3D Rendering Technology
The journey of 3D rendering technology is a testament to the rapid advancements in computing power and software algorithms. In the early days of computer graphics, rendering a single frame could take hours or even days. Today, real-time rendering engines can produce photorealistic images in milliseconds, enabling interactive experiences and revolutionizing industries like gaming and virtual reality.
One of the most significant milestones in this evolution was the introduction of ray tracing technology. By simulating the physical behavior of light, ray tracing allows for incredibly realistic lighting, reflections, and shadows. While once reserved for high-end production studios, ray tracing capabilities are now accessible to individual creators through consumer-grade hardware and software.
Another game-changing development has been the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into rendering processes. These technologies have dramatically reduced rendering times and improved image quality by intelligently predicting and optimizing rendering parameters. For instance, NVIDIA's DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) technology can upscale lower-resolution images to 4K or even 8K resolutions with minimal loss in quality, significantly reducing the computational resources required for high-fidelity rendering.
Blender: The Open-Source Powerhouse
When discussing essential apps for 3D rendering and visualization, it's impossible to overlook Blender. This open-source 3D creation suite has radically transformed recently, evolving from a niche tool to an industry-standard powerhouse. With its comprehensive feature set and zero cost, Blender has democratized 3D content creation, allowing aspiring artists and small studios to compete with established professionals.
Blender's Cycles Render Engine stands out for its ability to produce stunningly photorealistic results. In benchmark tests, Cycles has consistently performed on par with or even surpassed proprietary rendering engines costing thousands of dollars. The recent introduction of Cycles X, an optimized version of the Engine, has further improved rendering speeds by up to 8x on GPUs.
One of Blender's unique strengths is its vibrant community of developers and artists. This ecosystem has created thousands of add-ons and extensions, many of which are free or low-cost. For instance, the BlenderKit add-on provides access to a vast library of 3D models, materials, and HDRIs directly within the Blender interface, streamlining the asset creation process.
Blender's commitment to innovation is evident in its adoption of cutting-edge technologies. The software now includes a real-time render engine called EEVEE, which leverages modern GPU capabilities to provide near-instant feedback during creation. This has been a game-changer for artists working on time-sensitive projects or those requiring rapid iteration.
Unreal Engine: Beyond Gaming
While primarily known as a game development platform, Unreal Engine has emerged as a formidable tool for high-end visualization across various industries. Its real-time rendering capabilities, node-based material editor, and powerful Blueprint visual scripting system make it ideal for creating interactive architectural walkthroughs, product configurators, and virtual production sets.
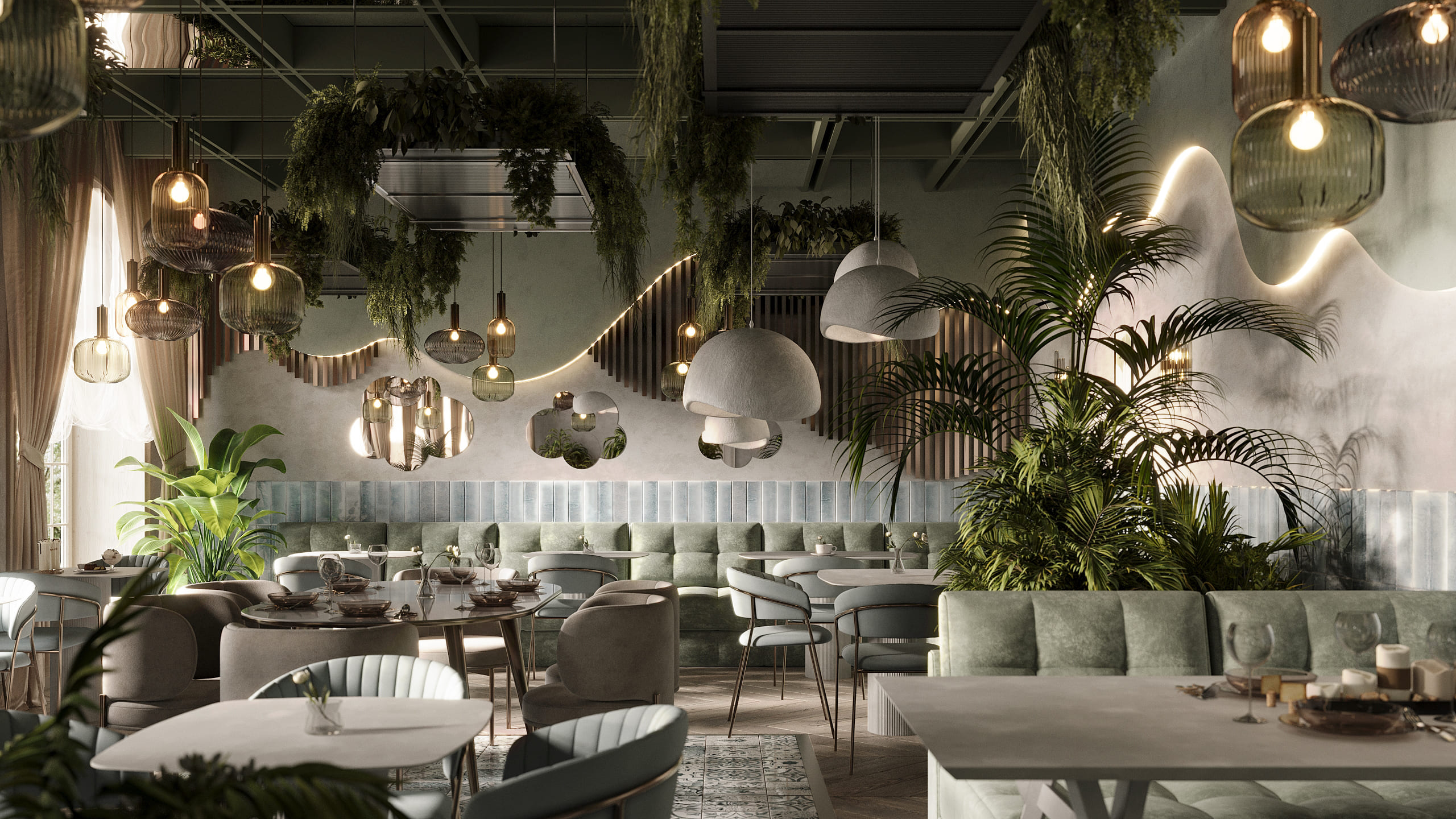

Image from Yousee Studio
Unreal Engine's Nanite virtualized geometry system has redefined the possibilities of real-time rendering. This technology allows for using film-quality assets containing millions of polygons without compromising performance. In practical terms, this means that architects can now create virtual environments with unprecedented detail, including intricate architectural elements and realistic landscapes, all running smoothly on consumer hardware.
The integration of path tracing in Unreal Engine 5 has further blurred the line between real-time and offline rendering. This technology simulates the behavior of light with such accuracy that it can produce results indistinguishable from traditional offline renderers but in real-time or near-real-time, depending on scene complexity.
Unreal Engine's impact on film and television cannot be overstated. The technology has been used in producing shows like The Mandalorian, where it powers LED wall backgrounds that react in real-time to camera movements, creating seamless integration between physical sets and digital environments. This approach has reduced post-production costs by up to 30% and shortened production schedules by weeks or months.
V-Ray: The Industry Standard for Photorealism
V-Ray remains the gold standard for professionals who demand the utmost in photorealistic rendering. Developed by Chaos Group, V-Ray is renowned for its physically accurate lighting simulation and advanced material system. Its ability to handle complex scenes with millions of polygons and hundreds of light sources makes it a favorite among architectural visualization specialists and visual effects artists.
V-Ray's strength lies in its versatility and integration with multiple 3D modeling software. Whether you're working in 3ds Max, Maya, SketchUp, or Rhino, V-Ray provides a consistent, high-quality rendering solution. This cross-platform compatibility has made it a choice for large studios with diverse software ecosystems.
One of V-Ray's most powerful features is its Global Illumination (GI) system. V-Ray can produce stunningly realistic ambient lighting and soft shadows by accurately simulating how light bounces and interacts within a scene. The latest version of V-Ray has introduced a new Light Cache algorithm that can reduce GI calculation times by up to 7x compared to previous versions, significantly speeding up the iterative design process.
V-Ray's material system is another area in which it excels. The VRayMtl shader provides granular control over surface properties, allowing artists to create everything from glossy car paint to translucent human skin. The introduction of the AI Denoiser has been a game-changer for many users, reducing render times by up to 50% while maintaining image quality.
Houdini: Procedural Modeling and Effects
While not strictly a rendering application, Houdini deserves a place in this discussion due to its powerful procedural modeling capabilities and impact on the visualization pipeline. Developed by SideFX, Houdini is renowned for its node-based workflow that allows artists to create complex, highly detailed 3D models and effects with remarkable efficiency.
Houdini's procedural approach to 3D creation sets it apart from traditional modeling software. Rather than manually crafting each scene element, artists can define rules and relationships that generate geometry automatically. This is particularly useful for creating large-scale environments, intricate architectural details, or natural phenomena like landscapes and vegetation.
The software's Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tools have revolutionized the creation of realistic destruction simulations. By accurately modeling the physical properties of materials, Houdini can generate believable debris and structural failures. This capability has been leveraged in numerous blockbuster films and high-end architectural visualizations.
Houdini's KineFX toolset has introduced a new paradigm for character animation and crowd simulation. By treating characters as a collection of interconnected rigid bodies, KineFX allows for more natural and dynamic movements, especially in large crowd scenes. This technology has been used to create stunning visual effects in films and games, with some productions reporting a 40% reduction in animation time for background characters.
The Rise of Cloud-Based Rendering
Many professionals turn to cloud-based rendering solutions as 3D scenes become increasingly complex and render times grow longer. Services like Chaos Cloud, Render Pool, and Amazon Web Services offer scalable rendering power that can significantly reduce turnaround times for large projects.
Cloud rendering has democratized access to high-performance computing resources. Small studios and freelancers can now tap into render farms with thousands of CPU and GPU cores, allowing them to complete projects that would have been impractical or impossible with local hardware. This has leveled the playing field, enabling smaller teams to compete with larger studios on render-intensive projects.
Cloud rendering offers substantial efficiency gains. A scene that might take days to render on a local workstation can be completed in hours or even minutes using a distributed cloud rendering system. This rapid turnaround allows for more iterations and refinements, ultimately leading to higher-quality final outputs.
However, cloud rendering has its challenges. Data security and intellectual property concerns have made some studios hesitant to adopt these services. Additionally, the cost structure of cloud rendering can be complex, with some providers charging by the minute or by the number of render nodes used. Careful management is required to ensure that cloud rendering remains cost-effective, especially for long-running or high-resolution projects.
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
The field of 3D rendering and visualization is constantly evolving, with new technologies promising to reshape the industry again. One of the most exciting developments is integrating machine learning and AI into the rendering pipeline. For example, NVIDIA's OptiX AI-Accelerated Denoiser can dramatically reduce render times by intelligently removing noise from partially rendered images, producing clean results in a fraction of the time required for traditional methods.
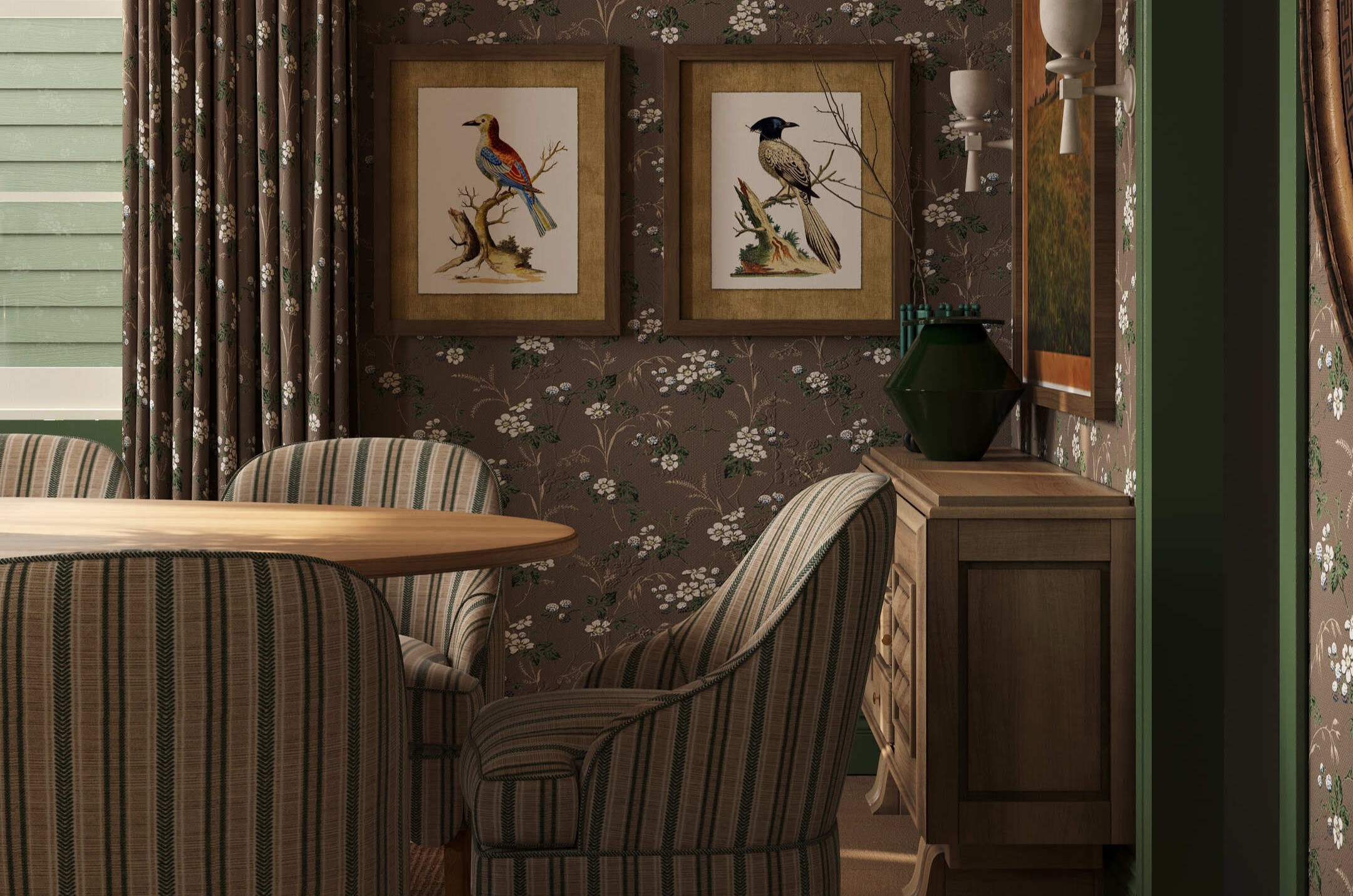

Image from Yousee Studio
Another area of innovation is the development of hybrid rendering techniques that combine the speed of rasterization with the accuracy of ray tracing. These approaches aim to provide the best of both worlds, offering real-time performance with near-photorealistic quality. Technologies like Unreal Engine's Lumen global illumination system exemplify this trend, providing dynamic, high-quality lighting that adapts in real time to changes in the scene.
The increasing adoption of virtual and augmented reality also drives innovation in rendering technology. As these platforms demand high frame rates and low latency, rendering engines are optimized for performance on mobile devices and standalone VR headsets. This has led to the development of techniques like foveated rendering, which concentrates rendering resources on the area of the image where the user is looking, reducing overall computational demands.
Conclusion
The world of 3D rendering and visualization is constantly changing, with new technologies and applications emerging rapidly. From the democratizing influence of open-source tools like Blender to the cutting-edge capabilities of industry stalwarts like V-Ray and Houdini, creators have access to an unprecedented array of robust software solutions.
As we look to the future, it's clear that the boundaries between different types of visualization software are becoming increasingly blurred. Real-time engines adopt features traditionally associated with offline renderers, while traditional 3D packages integrate more interactive and real-time capabilities. This convergence creates new opportunities for artists and designers to push the boundaries of what's possible in digital visualization.
The key to success in this evolving landscape lies in adaptability and a willingness to embrace new technologies and workflows. Whether you're an architect creating immersive virtual walkthroughs, a product designer crafting photorealistic prototypes, or a visual effects artist bringing impossible worlds to life, the tools discussed in this article provide a solid foundation for creating stunning 3D visualizations. As these technologies continue to advance, we can only imagine the incredible visual experiences that lie ahead.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Ray Lisbon is a content writer and the author of this article.