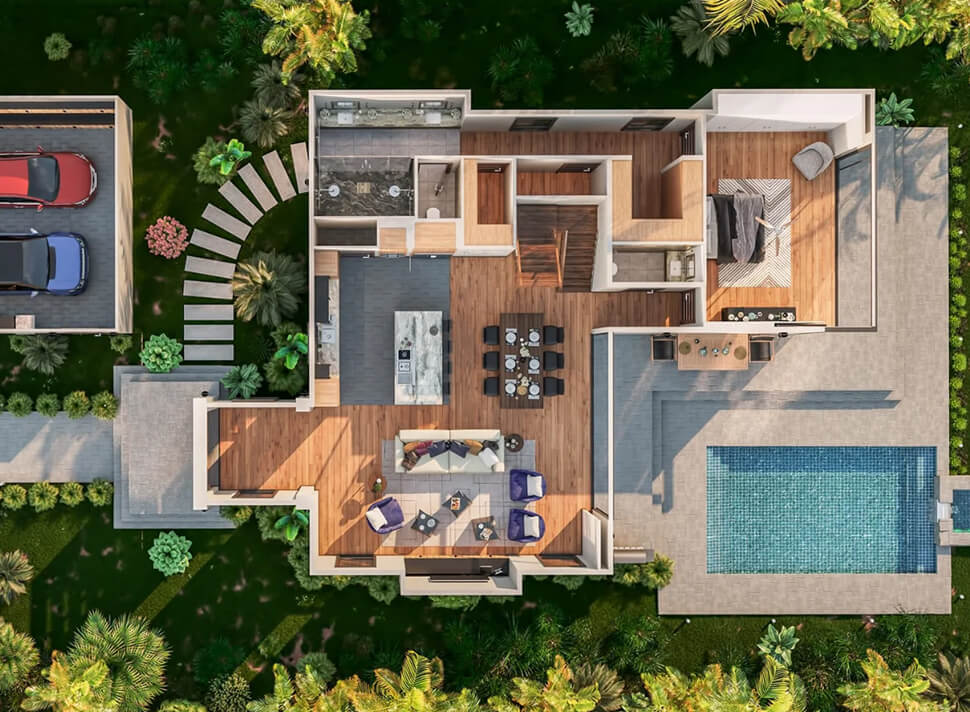
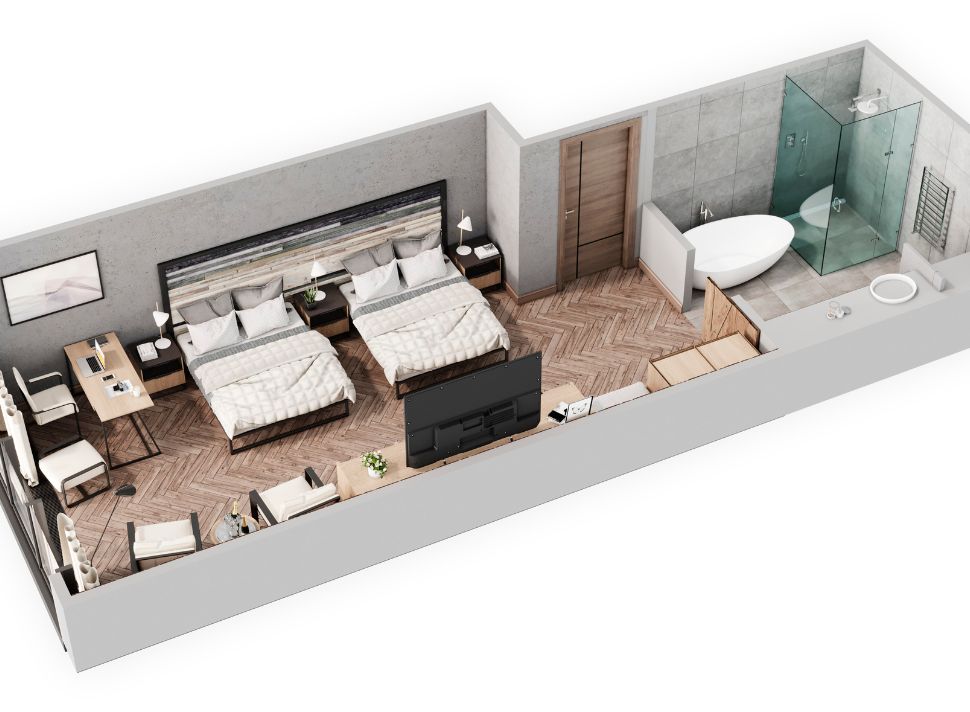
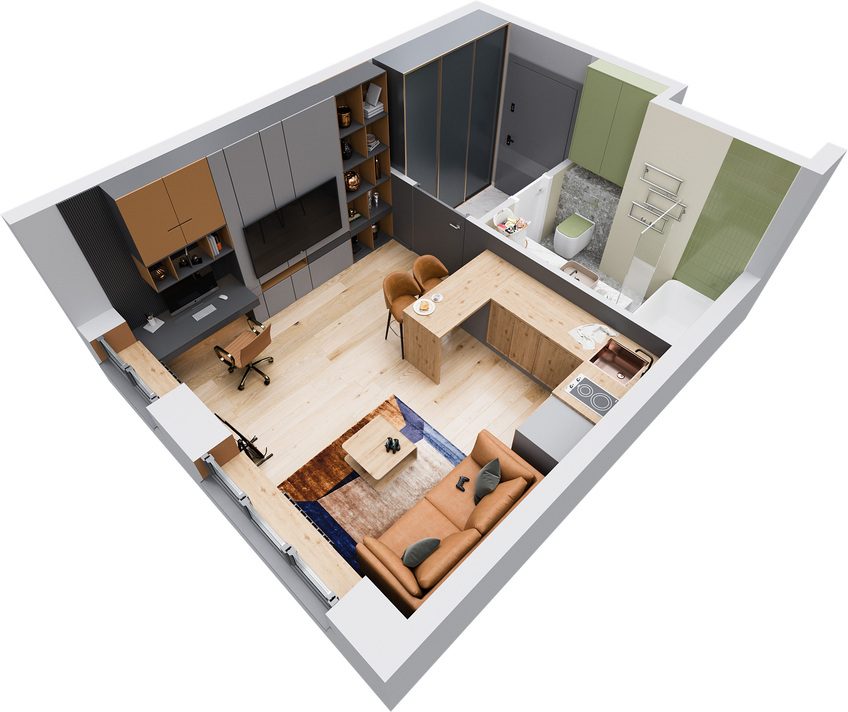
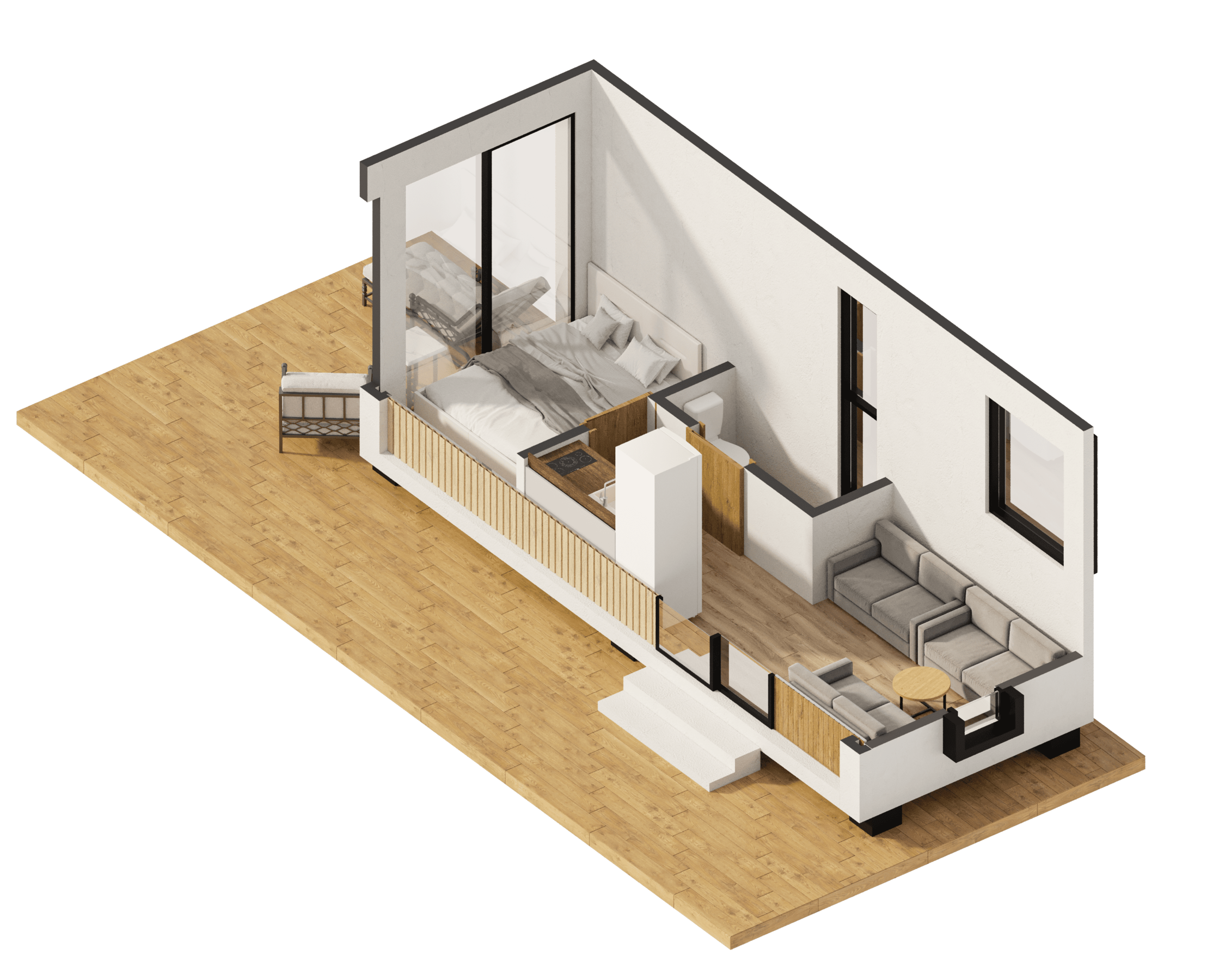
Harnessing AI to Perfect 3D Floor Plan Accuracy
At YouSee Studio, we are currently investigating the potential of AI technologies to enhance our traditional 3D modeling processes. This article provides insights into potential AI applications in 3D rendering, reflecting our commitment to innovation and excellence.
In the ever-evolving landscape of architectural design and spatial planning, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changing force, particularly in 3D floor plan creation. Human error, time-consuming processes, and limitations in accuracy have long plagued the traditional methods of crafting floor plans. However, the advent of AI-driven technologies has ushered in a new era of precision and efficiency, revolutionizing how we conceptualize and visualize spatial layouts.
The AI Revolution in Spatial Design
The concept of a 3D floor plan has transcended its humble origins as a simple two-dimensional sketch. Today, it is a sophisticated, immersive representation of architectural spaces, offering stakeholders a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships, dimensions, and aesthetics. Integrating AI into this process has enhanced the accuracy of these plans and opened up new possibilities for innovation and creativity in design.
AI algorithms, powered by machine learning and computer vision, can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make intelligent decisions in real-time. When applied to 3D floor plan creation, these algorithms can process complex spatial information, automatically detect and correct inconsistencies, and generate highly accurate representations of interior spaces.
Deep Learning and Spatial Recognition
One of the most promising applications of AI in 3D floor plan accuracy is the use of deep learning algorithms for spatial recognition. These advanced neural networks can be trained on extensive datasets of architectural plans, building codes, and real-world spatial configurations. By learning from this diverse information, AI systems can better understand spatial relationships and architectural norms.
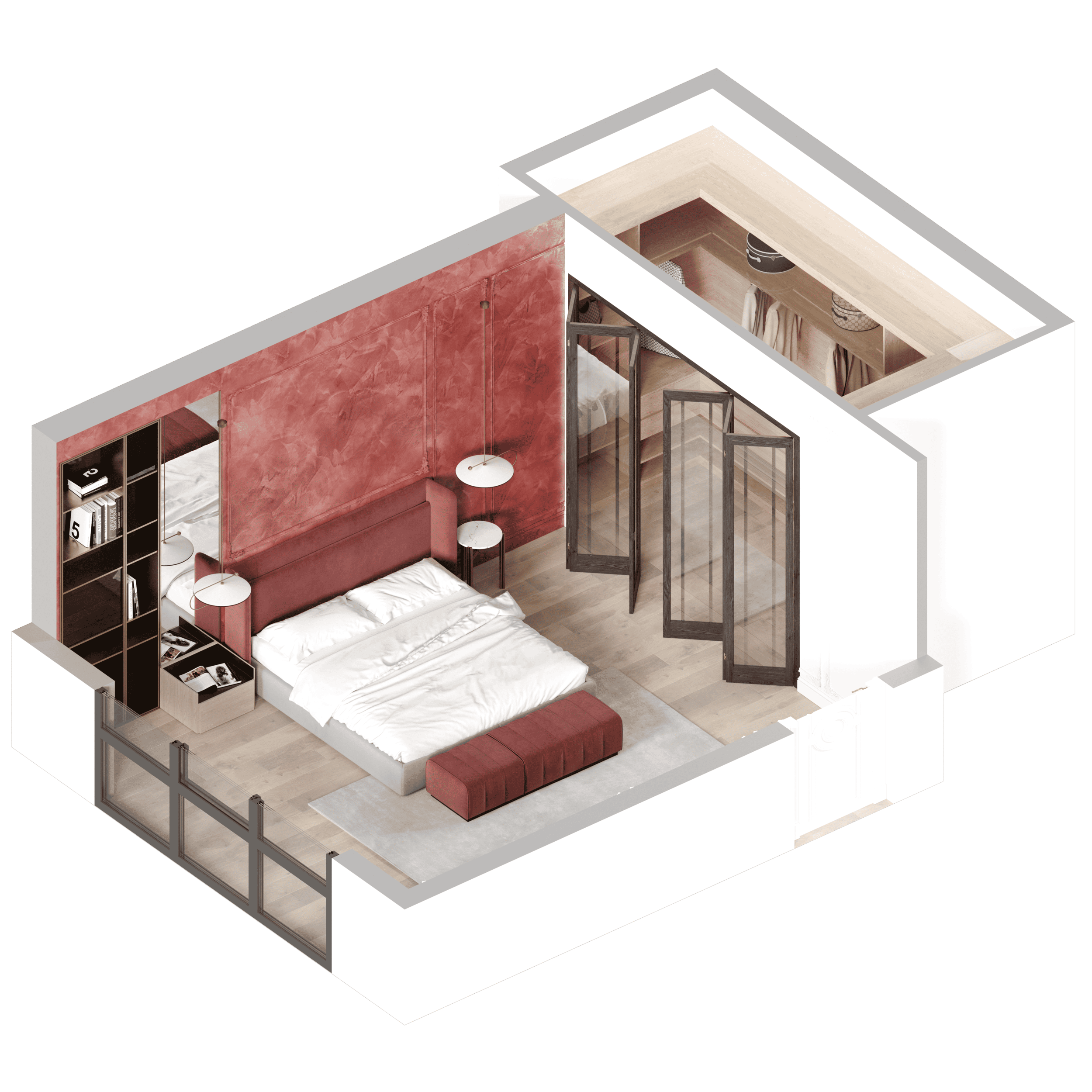
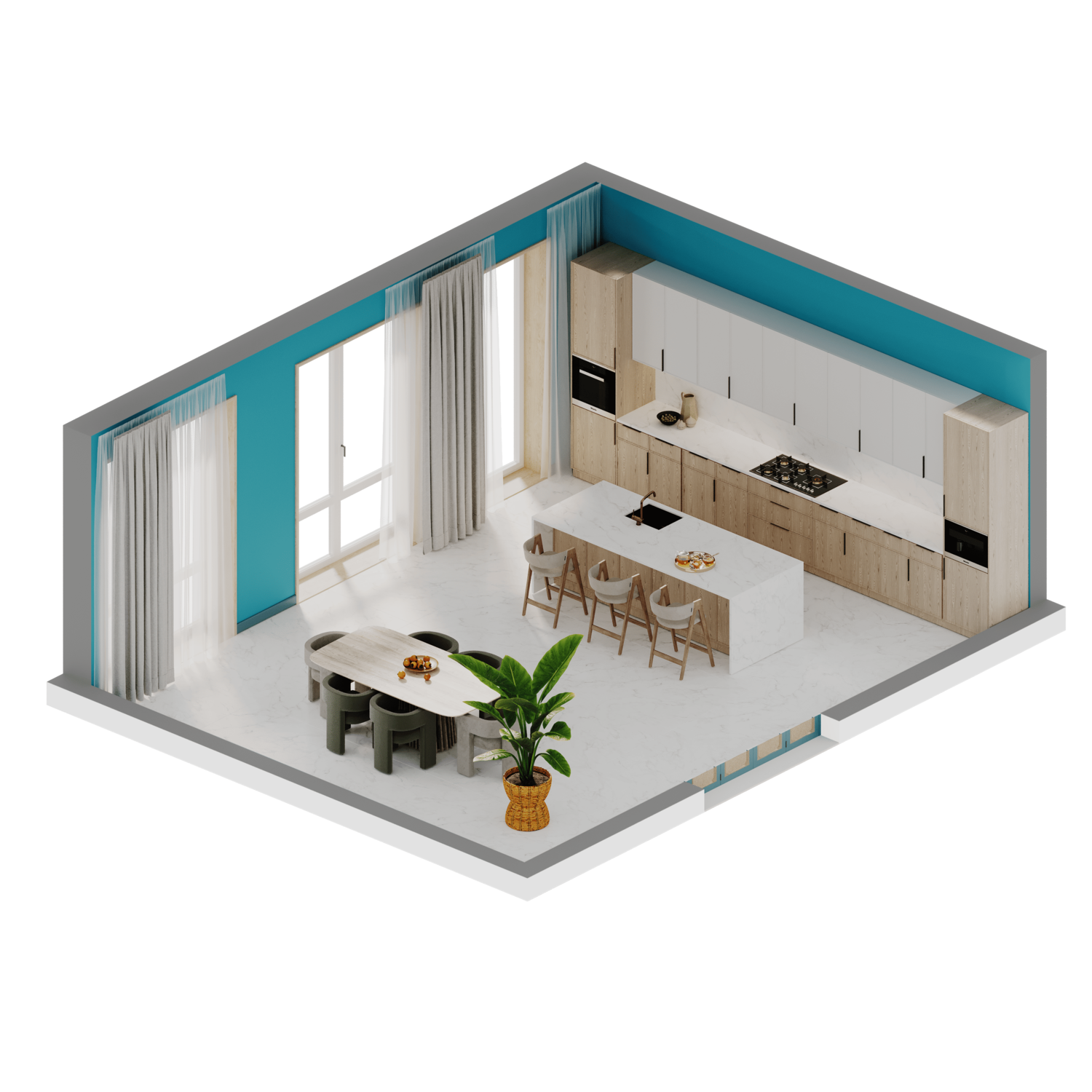
Image from Yousee Studio
For instance, a deep learning model trained on millions of floor plans can quickly identify common elements such as walls, doors, windows, and fixtures. This capability allows the AI to automatically generate accurate 3D floor plans from various input sources, including 2D sketches, photographs, or even laser scans of existing spaces.
In a recent study by the Institute of Architectural Intelligence, researchers found that AI-powered spatial recognition systems achieved an accuracy rate of 98.7% in identifying and categorizing architectural elements, compared to a 92.3% accuracy rate for human experts. This significant improvement in accuracy translates to more reliable and precise 3D floor plans, reducing the need for time-consuming manual corrections and revisions.
AI-Enhanced Parametric Design
Parametric design principles are another groundbreaking application of AI in 3D floor plan creation. Parametric design involves defining and manipulating relationships between different design elements, allowing for complex and dynamic architectural solutions. AI algorithms can enhance this process by optimizing these relationships based on predefined parameters and constraints.
For example, an AI-powered parametric design system can automatically adjust room layouts, furniture placement, and circulation paths to maximize space efficiency while adhering to building codes and design guidelines. This optimization level would be incredibly time-consuming and complex for human designers to achieve manually.
The impact of AI-enhanced parametric design on 3D floor plan accuracy is substantial. In a recent project by the architectural firm NeuroSpace Designs, implementing an AI-driven parametric system resulted in a 40% reduction in spatial conflicts and a 25% improvement in overall space utilization compared to traditional design methods.
Real-Time Error Detection and Correction
One of the most significant advantages of incorporating AI into 3D floor plan creation is the ability to perform real-time error detection and correction. Traditional methods often rely on manual checks and revisions, which can be time-consuming and prone to oversight. AI algorithms, however, can continuously analyze the developing floor plan, identifying potential issues such as spatial conflicts, code violations, or structural inconsistencies as they arise.
These AI systems can be programmed with comprehensive knowledge of building codes, accessibility requirements, and design best practices. As the 3D floor plan is being created or modified, the AI can instantly flag deviations from these standards and suggest corrections. This real-time feedback loop ensures that accuracy is maintained throughout the design process rather than relying on post-design quality control measures.
A study by the Architectural Technology Institute found that AI-powered error detection systems reduced the average time spent on plan revisions by 62% while increasing overall plan accuracy by 28%. This dramatic improvement in efficiency and accuracy has significant implications for the architectural design industry, potentially saving millions of dollars in project costs and reducing construction delays caused by design errors.
AI-Driven Dimensional Accuracy
Precise measurements are crucial in creating accurate 3D floor plans, and AI excels in this area. By leveraging computer vision and machine learning algorithms, AI systems can extract highly accurate dimensional data from various sources, including laser scans, photogrammetry, and smartphone cameras.
These AI-powered measurement systems can process complex spatial data in seconds, generating precise 3D models with minimal human intervention. For example, the AI-based software DimensionAI can create a detailed 3D floor plan from a series of smartphone photos with an average accuracy of ±0.5 inches, a level of precision that would be challenging to achieve consistently with manual measurements.
Furthermore, AI algorithms can automatically adjust for familiar sources of measurement error, such as lens distortion or perspective skew in photographs. This capability ensures that the resulting 3D floor plans maintain high dimensional accuracy, even when working with imperfect input data.
Intelligent Space Optimization
Beyond merely representing existing spaces, AI can be crucial in optimizing spatial layouts for various purposes. AI algorithms can generate multiple layout options that maximize space efficiency and usability by analyzing user requirements, traffic flow patterns, and functional relationships between different areas.
These AI-driven optimization processes can consider a wide range of factors, including:
- Natural light distribution
- Acoustic properties
- Energy efficiency
- Accessibility requirements
- Ergonomic considerations
For instance, an AI system developed by SpaceLogic Technologies demonstrated the ability to generate office layout designs that increased productivity by 15% and reduced energy consumption by 22% compared to traditional layouts. This optimization level is achieved by analyzing vast amounts of data on human behavior, workplace dynamics, and environmental factors – a task that would be virtually impossible for human designers to perform manually with the same degree of thoroughness and accuracy.
AI-Assisted Material Selection and Visualization
Accurate 3D floor plans go beyond mere spatial representation and involve the realistic visualization of materials, textures, and finishes. AI algorithms can significantly enhance floor plan creation by suggesting appropriate materials based on design style, budget constraints, and functional requirements.
Moreover, AI-powered rendering engines can generate photorealistic visualizations of these materials in the context of the 3D floor plan. This capability allows stakeholders to make more informed decisions about design choices and ensures that the final product accurately reflects the space's intended aesthetic and functional qualities.

Image from Yousee Studio
A recent survey of architectural firms found that those utilizing AI-assisted material selection and visualization tools reported a 37% increase in client satisfaction and a 45% reduction in the number of design revisions requested during the project lifecycle.
Conclusion: The Future of 3D Floor Plan Accuracy
As we look to the future, AI's role in perfecting 3D floor plan accuracy is set to expand even further. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing and neuromorphic hardware promise to unlock new levels of computational power, enabling AI systems to process and analyze spatial data with unprecedented speed and complexity.
The integration of AI into 3D floor plan creation is not just about improving accuracy—it's about fundamentally transforming the way we approach spatial design. By harnessing the power of machine learning, computer vision, and advanced algorithms, we are entering an era in which the boundaries between imagination and realization are becoming increasingly blurred.
As AI evolves and becomes more sophisticated, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in architectural design and spatial planning. The possibilities are limitless, from AI-generated architectural concepts to self-optimizing buildings that adapt to changing environmental conditions.
In conclusion, harnessing AI to perfect 3D floor plan accuracy represents a significant leap forward in architectural design and spatial planning. By leveraging the power of artificial intelligence, we are improving the precision and efficiency of floor plan creation and unlocking new realms of creativity and innovation in spatial design. As we continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with AI-driven technologies, we can look forward to a future where our built environments are more accurate, efficient, and responsive to human needs than ever before.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Karen Spacey is a content writer and the author of this article.