What is Rendering in Interior Design and Why It Matters
In interior design, creating visually stunning and conceptually rich spaces is at the core of every project. Interior designers possess the remarkable ability to transform mere physical structures into immersive environments that resonate with aesthetics and functionality. One of the pivotal tools that enable this transformation is rendering. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of generating in interior design, exploring what it entails, its significance in the design process, and why it matters more than ever in the digital age.
The Essence of Rendering
Rendering Defined
At its essence, rendering generates a visual representation of an object or environment from a model. Interior design involves creating highly detailed and realistic images or animations that depict how a space will look after it's been designed and furnished.
The Art of Visualization
Rendering is the art of turning imagination into reality, allowing designers to make visualization interiors their concepts with remarkable precision. It bridges the gap between a mere idea on paper and a tangible, almost lifelike representation of the final design. It's the tool that transforms sketches and plans into compelling visual narratives that clients can understand and appreciate.
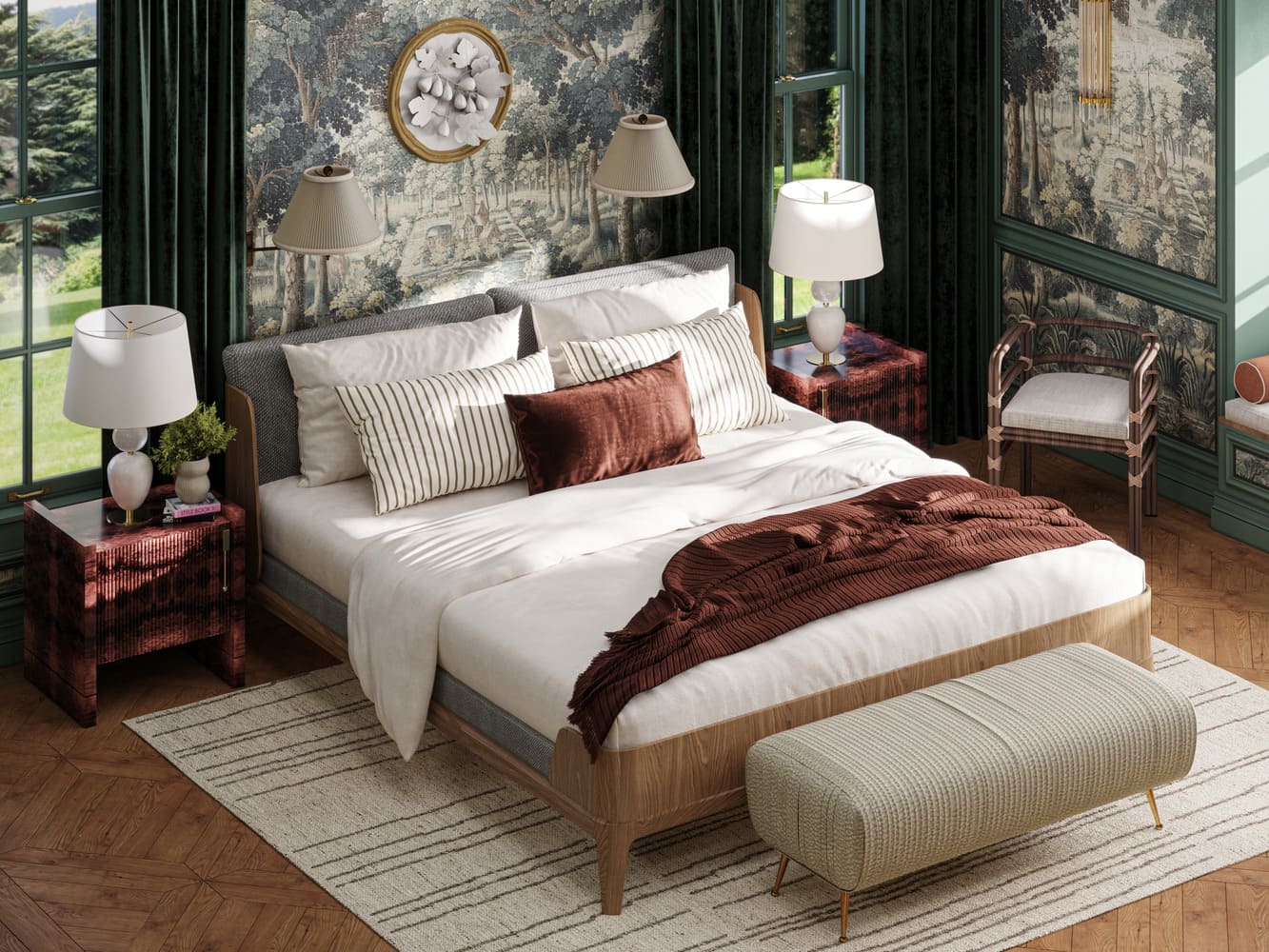

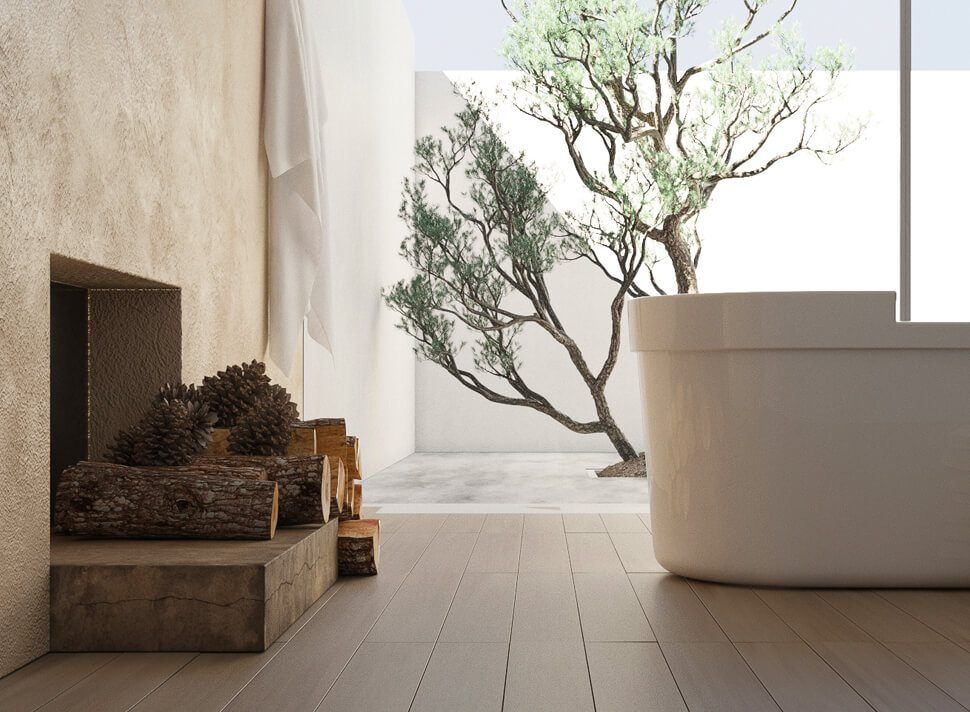
Image from Yousee Studio
The Evolution of Rendering
Rendering has a rich history dating back to the earliest forms of artistic expression. Artists, architects, and designers have used various historical rendering techniques to communicate their visions. However, in the contemporary world of interior design, rendering has evolved significantly thanks to technological advancements.
The Significance of Rendering in Interior Design
Communication and Concept Presentation
Imagine explaining a complex interior design concept to a client using only words or 2D drawings. It's often challenging to convey the whole essence of a design solely through these means. This is where rendering shines. It provides a visual language that speaks to everyone, regardless of their familiarity with design or technical drawings. Clients can see exactly how their space will look and feel, which enhances communication and ensures that everyone is on the same page.
Design Development and Refinement
Rendering is not just about presentation; it's an integral part of the design process. Designers use rendering to experiment with different materials, color schemes, lighting scenarios, and furniture layouts. They can make quick changes and see the immediate impact on the space. This flexibility significantly speeds up the design development phase and allows for more precise decision-making.
Problem-Solving
Renderings also serve as powerful problem-solving tools. They enable designers to identify potential issues before they become costly problems during construction or renovation. For example, a rendering might reveal that a particular lighting scheme creates unwanted shadows or that a chosen color palette clashes with the intended mood of the space. Identifying and addressing these issues early in the design phase can save time and money.
The Tools of the Trade
Software Solutions
In the modern era of interior design, rendering is predominantly a digital endeavor. Powerful software tools like AutoCAD, SketchUp, 3ds Max, and Revit have become indispensable for designers. These applications allow for the creation of highly detailed 3D models that serve as the foundation for renderings.
Visualization Plugins
Designers often turn to specialized visualization plugins to take rendering to the next level. Software like V-Ray, Lumion, and Enscape can produce photorealistic renderings and even real-time walkthroughs of 3D models. These plugins leverage advanced algorithms to simulate how light interacts with materials, resulting in stunningly lifelike images.
Hardware Advancements
Rendering, especially at the highest levels of realism, demands significant computational power. Designers use high-performance computers with powerful GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and CPUs (Central Processing Units) to meet this need. These machines can crunch complex rendering calculations quickly, reducing the time required to generate images.
Types of Rendering in Interior Design
Still Renderings
Still renderings are static images depicting a single interior space view. They are the most common type of rendering used in internal design presentations. These images provide a clear snapshot of a room's appearance when completed.
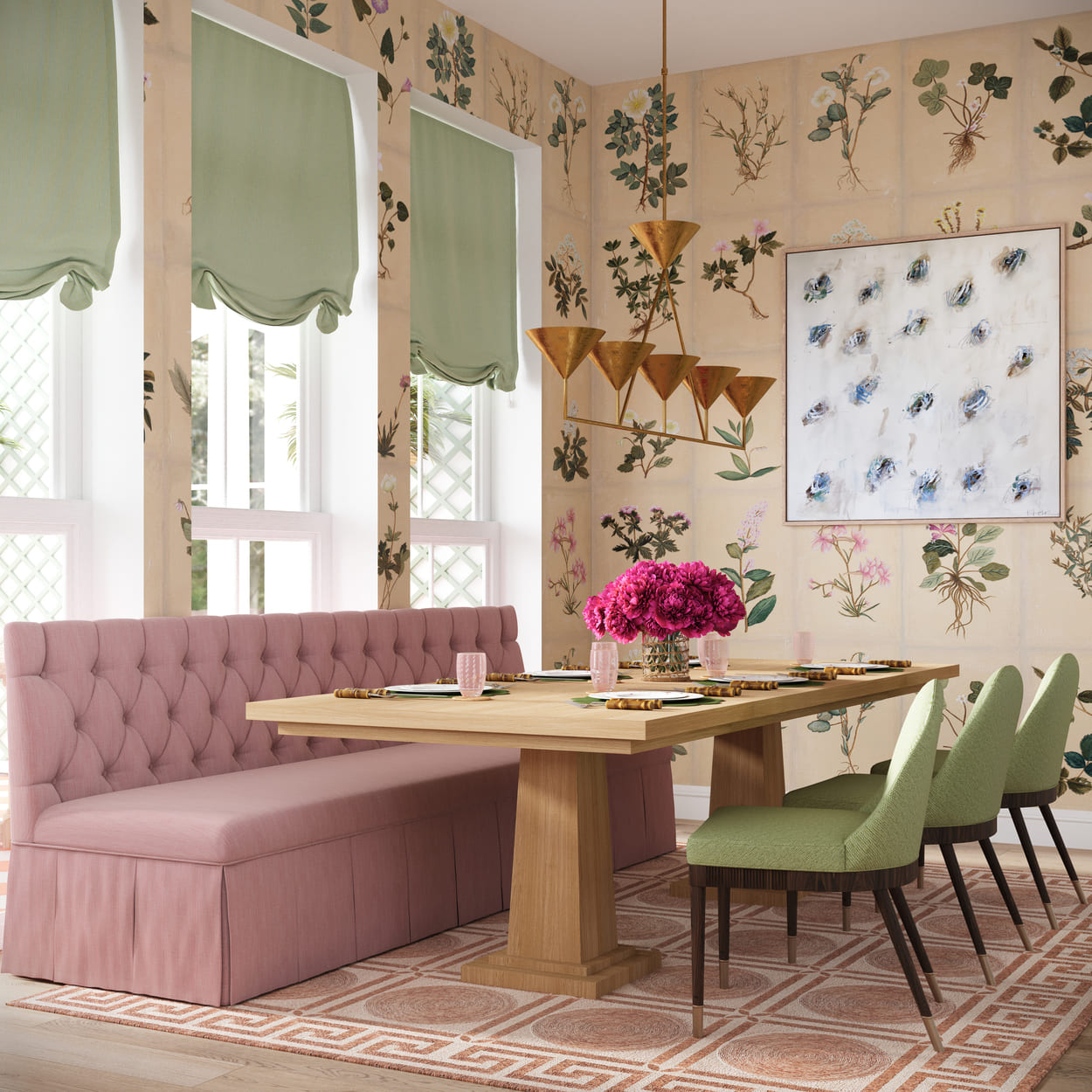

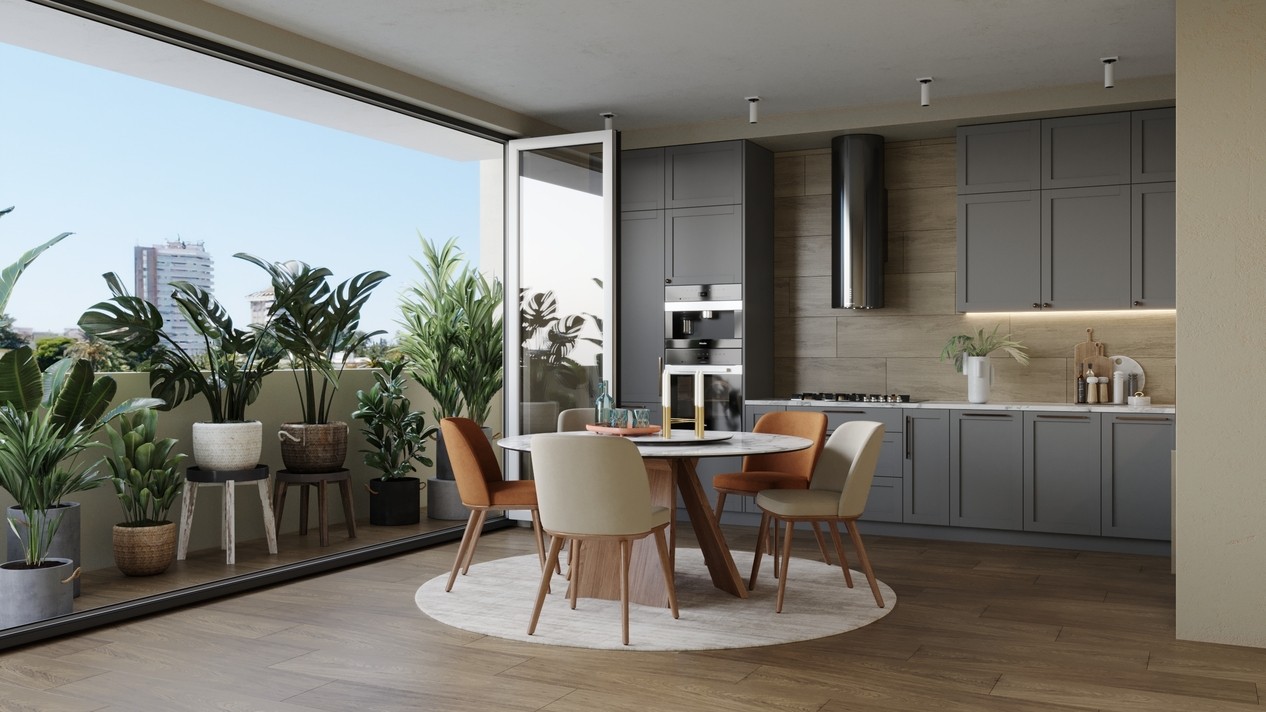
Image from Yousee Studio
360-Degree Renderings
Also known as panoramic renderings, these images allow viewers to navigate through an entire room in a single image. They provide an immersive experience and are often used in marketing materials or websites to showcase a space.
Animated Renderings
Incorporating animation into renderings brings a dynamic element to the visualization. Designers can create fly-throughs, walk-throughs, or even videos that showcase the space from multiple angles, giving clients a comprehensive view of the design.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR are becoming increasingly popular in interior design as technology advances. With VR, clients can don a headset and walk through a virtual representation of their future space. AR, on the other hand, overlays digital information in the real world, allowing clients to visualize design elements within their existing environment.
In the second part of our guide, we will explore the practical aspects of rendering in interior design, from choosing the right software and hardware to understanding the process of creating stunning renderings that captivate clients and elevate your design projects to new heights.
Choosing the Right Software
Selecting the appropriate software is the first crucial step in mastering the art of interior rendering. Different software options cater to various aspects of the rendering process, from 3D modeling to lighting simulation and final image generation. Here are some popular choices:
1. AutoCAD:
- Strengths: AutoCAD is renowned for its precision in 2D drafting and 3D modeling. It forms a solid foundation for creating accurate 3D models that can later be rendered.
- Considerations: While AutoCAD is excellent for modeling, it may require additional plugins or external rendering software for photorealistic results.
2. SketchUp:
- Strengths: SketchUp is known for its user-friendly interface and quick modeling capabilities. It's a favorite among designers for creating initial 3D representations of spaces.
- Considerations: SketchUp often integrates with advanced rendering plugins like V-Ray or Enscape.
3. 3ds Max:
- Strengths: 3ds Max is a comprehensive 3D modeling and rendering software. It's favored for its flexibility in creating complex 3D scenes and animations.
- Considerations: It has a steeper learning curve than SketchUp but offers more advanced rendering features.
4. Revit:
- Strengths: Revit is tailored for architecture and building information modeling (BIM). It's ideal for creating highly detailed building models that can be used for rendering.
- Considerations: While Revit has rendering capabilities, designers often use external software like V-Ray for more sophisticated results.
5. Blender:
- Strengths: Blender is an open-source 3D creation suite. It offers powerful modeling and rendering capabilities and is entirely free to use.
- Considerations: Due to its versatility, Blender can be complex for beginners, but it's an excellent choice for those looking for a robust, no-cost solution.
6. V-Ray:
- Strengths: V-Ray is a renowned rendering plugin compatible with various 3D modeling software. It excels in creating photorealistic images and is widely used in the industry.
- Considerations: While V-Ray is a paid plugin, its rendering quality justifies the cost for professionals.
7. Enscape:
- Strengths: Enscape is known for its real-time rendering capabilities. It seamlessly integrates with popular design software like Revit, SketchUp, and Rhino.
- Considerations: Enscape prioritizes speed and ease of use, making it an excellent choice for design presentations.
Choosing the right software depends on your specific needs, familiarity with the program, and the desired level of realism for your renderings. Many designers use a combination of software tools to maximize their capabilities.
Building Your 3D Model
Once you've selected your software, the next step is to create a detailed 3D model of the interior space you're designing. The level of detail in your model will significantly impact the quality of your renderings. Here are some key considerations:
1. Precision in Modeling:
- Ensure your 3D model accurately represents the physical space, including dimensions, proportions, and architectural features. Precision is crucial for realistic renderings.
2. Materials and Textures:
- Assign appropriate materials and textures to objects in your model. Wood should look like wood, metal like metal, and so on. Pay attention to how materials interact with lighting.
3. Lighting Setup:
- Set up the lighting within your 3D model as realistically as possible. Consider the position and type of light fixtures, natural lighting, and the time of day your rendering should represent.
4. Camera Placement:
- Position the camera within your 3D model to capture the desired view. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find the most compelling composition.
5. Furniture and Décor:
- Furnish and decorate the space with appropriate furniture, fixtures, and decor items. These details add realism and help clients visualize the final design.
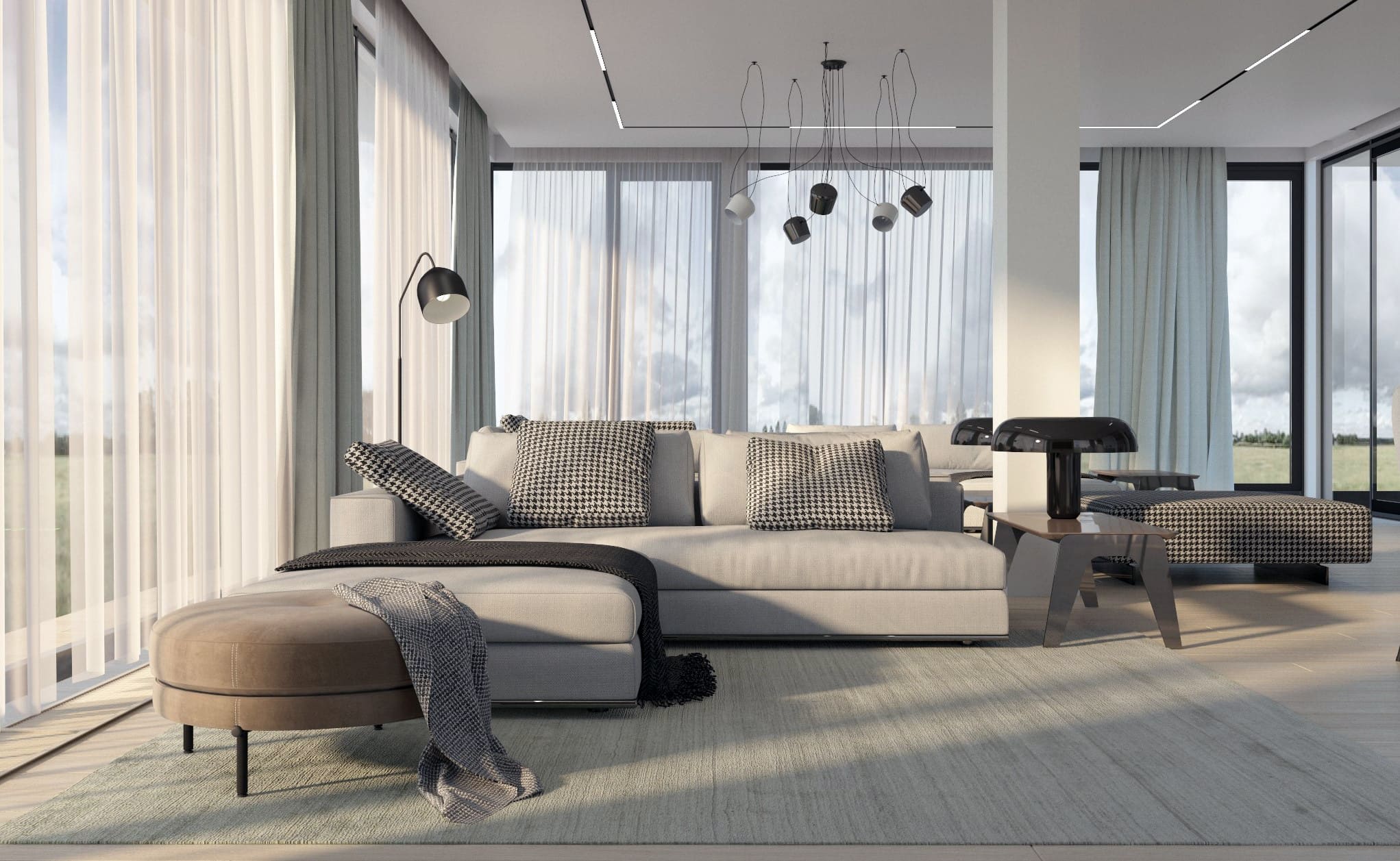

Image from Yousee Studio
Rendering Techniques
With your 3D model in place, it's time to explore rendering techniques that will bring your interior design to life. Here are some fundamental aspects to consider:
1. Render Settings:
- Most rendering software allows you to adjust various settings, such as image resolution, quality, and rendering time. Balance these settings to achieve the desired output while managing your project timeline.
2. Lighting:
- Lighting plays a pivotal role in rendering. Experiment with different lighting scenarios to create the ambiance you want. Understand how lighting affects materials and textures.
3. Materials and Textures:
- Fine-tune materials and textures in your model to achieve realism. Understand properties like roughness, reflectivity, and transparency and adjust them accordingly.
4. Camera Effects:
- Explore camera effects like depth of field and focal length to add depth and visual interest to your renderings. These effects mimic real-world photography techniques.
5. Post-Processing:
- After rendering, consider post-processing techniques in image editing software like Adobe Photoshop. These can enhance the final image, adjusting colors, contrast, and adding effects.
6. Real-Time Rendering:
- If time is a critical factor, consider real-time rendering options like Enscape. Real-time rendering allows you to make immediate changes and see the results instantly.
Client Engagement through Renderings
One of the primary reasons for creating interior renderings is to engage clients and ensure they fully understand and appreciate your design concept. Here are ways to leverage renderings for effective client communication:
1. Presentations:
- Use renderings during client presentations to walk them through the design. Highlight key features and design elements and explain how they contribute to the overall aesthetic.
2. Options and Alternatives:
- Render different design options or color schemes to help clients make informed decisions. Visualizing alternatives can be invaluable in the decision-making process.
3. Virtual Walkthroughs:
- If you have the capability, offer virtual walkthroughs using VR technology. This immersive experience allows clients to step into their future space and explore it firsthand.
4. Feedback and Revisions:
- Encourage clients to provide feedback based on renderings. It's often easier for clients to express their preferences when they can see the design in detail. Use their input to make revisions.
5. Marketing and Promotion:
- Use renderings in your marketing materials, website, and social media to showcase your design portfolio. High-quality renderings can attract potential clients and collaborators.
Challenges and Solutions
While rendering offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial and critical to mastering the art of interior rendering:
1. Rendering Time:
- Photorealistic renderings can be time-consuming, especially for complex scenes. Invest in powerful hardware or consider cloud rendering services to speed up the process.
2. Learning Curve:
- Rendering software often has a learning curve. Invest time learning the intricacies of your chosen software, or consider training courses.
3. Cost:
- High-quality rendering software and hardware can be expensive. Consider the return on investment (ROI) regarding client satisfaction and project success.
4. Realism vs. Speed:
- Balancing realism with rendering speed can be challenging. Understand project requirements and client expectations to strike the right balance.
Embracing Real-Time Rendering
Real-time rendering technology has revolutionized the rendering process. It allows designers to make changer 3D models and instantly see the results, making it an invaluable tool for efficient design iterations and client collaboration. Here are some ways to embrace real-time rendering:
1. Enscape for Real-Time Visualization:
- Enscape is a leading real-time rendering plugin that seamlessly integrates with popular design software like Revit, SketchUp, and Rhino. Its intuitive interface and speed make it a favorite among designers.
2. VR Integration:
- Take advantage of virtual reality (VR) integration with real-time rendering. With VR headsets, clients can immerse themselves in your design, providing an unparalleled sense of scale and presence.
3. Live Design Review Sessions:
- Conduct live design review sessions with clients using real-time rendering. Make changes on the fly and receive instant feedback, reducing design revision cycles.
Achieving Photorealism
Photorealistic renderings are the gold standard in interior design. They mimic real-world lighting, materials, and textures to create images that are virtually indistinguishable from photographs. Here's how to achieve photorealism:
1. High-Quality Textures:
- Invest in high-quality texture libraries or create custom textures for material fabric and metal. Pay materials attention to details like bump maps and displacement maps for added realism.
2. Advanced Lighting Simulation:
- Use advanced lighting simulation tools to replicate natural lighting conditions accurately. Experiment with different times of day to capture the ideal lighting scenario.
3. Material Accuracy:
- Understand the physical properties of materials and replicate them accurately in your 3D models. This includes attributes like reflectivity, transparency, and roughness.
4. Post-Processing Techniques:
- Apply post-processing techniques in image editing software to enhance the final rendering. Methods include color correction, contrast adjustment, and adding lens effects.
5. Realistic Camera Settings:
- Mimic real-world photography by adjusting camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. These settings impact depth of field and exposure, adding to the realism.
Exploring Animation and Cinematics
Static renderings are powerful, but animation takes the viewer on a path in the designed space. Interior design animations can showcase various aspects of a project, from the flow of space to the functionality of furniture. Here's how to explore animation and cinematics:
1. Camera Animation:
- Animate the camera to create dynamic walkthroughs of your interior spaces. Use smooth camera movements to guide viewers through the design.
2. Furniture and Object Animation:
- Animate furniture and objects within your 3D model to demonstrate functionality. For example, show how a sofa can be transformed into a bed.
3. Lighting and Time-Lapse:
- Experiment with lighting changes and time-lapse animations to showcase different moods and moments in a space. Highlight the transition from day to night, for instance.
4. Storytelling:
- Craft a narrative for your interior animation. Tell a story that engages viewers and helps them connect emotionally with the design.
The Rise of Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality is gaining traction in interior design. AR apps and platforms allow clients to visualize design concepts in their physical spaces. Here's how to leverage AR:
1. AR Design Apps:
- Explore AR design apps that let clients use their smartphones or tablets to superimpose virtual furniture and decor in their natural environments.
2. Interactive AR:
- Create interactive AR experiences enabling clients to walk virtually their future spaces using AR headsets or mobile devices.
3. Material Selection:
- Use AR to help clients choose materials by showing how different options will look in their actual. This can aid in decision-making and reduce design changes later.
Sustainability Visualization
Sustainability is a growing concern in interior design, and renderings can play a role in visualizing sustainable design choices. Here's how:
1. Eco-Friendly Materials:
- Showcase the friendly materials like reclaimed wood or recycled textiles in your renderings. Highlight the sustainability aspect of your design.
2. Energy Efficiency:
- Use renderings to demonstrate how energy-efficient features like LED lighting and intelligent climate control systems contribute to sustainability.
3. Green Spaces:
- Create renderings that emphasize indoor green spaces, such as living walls or indoor gardens, to promote a connection to nature and well-being.
Collaborative Virtual Design Spaces
With the rise of remote work and virtual collaboration, consider creating collaborative virtual design spaces. These platforms allow designers and clients to meet in virtual environments to review designs and make decisions together.
In conclusion, interior rendering has evolved and is a multifaceted tool for interior designers. By embracing real-time rendering, striving for photorealism, exploring animation and cinematics, leveraging augmented reality, visualizing sustainability, and adopting collaborative virtual design spaces, designers can push the boundaries of what's possible in interior rendering. These advanced techniques channeled communication and helped singers create more immersive and engaging interior spaces. As technology continues to advance, so do the possibilities for interior rendering in the design.
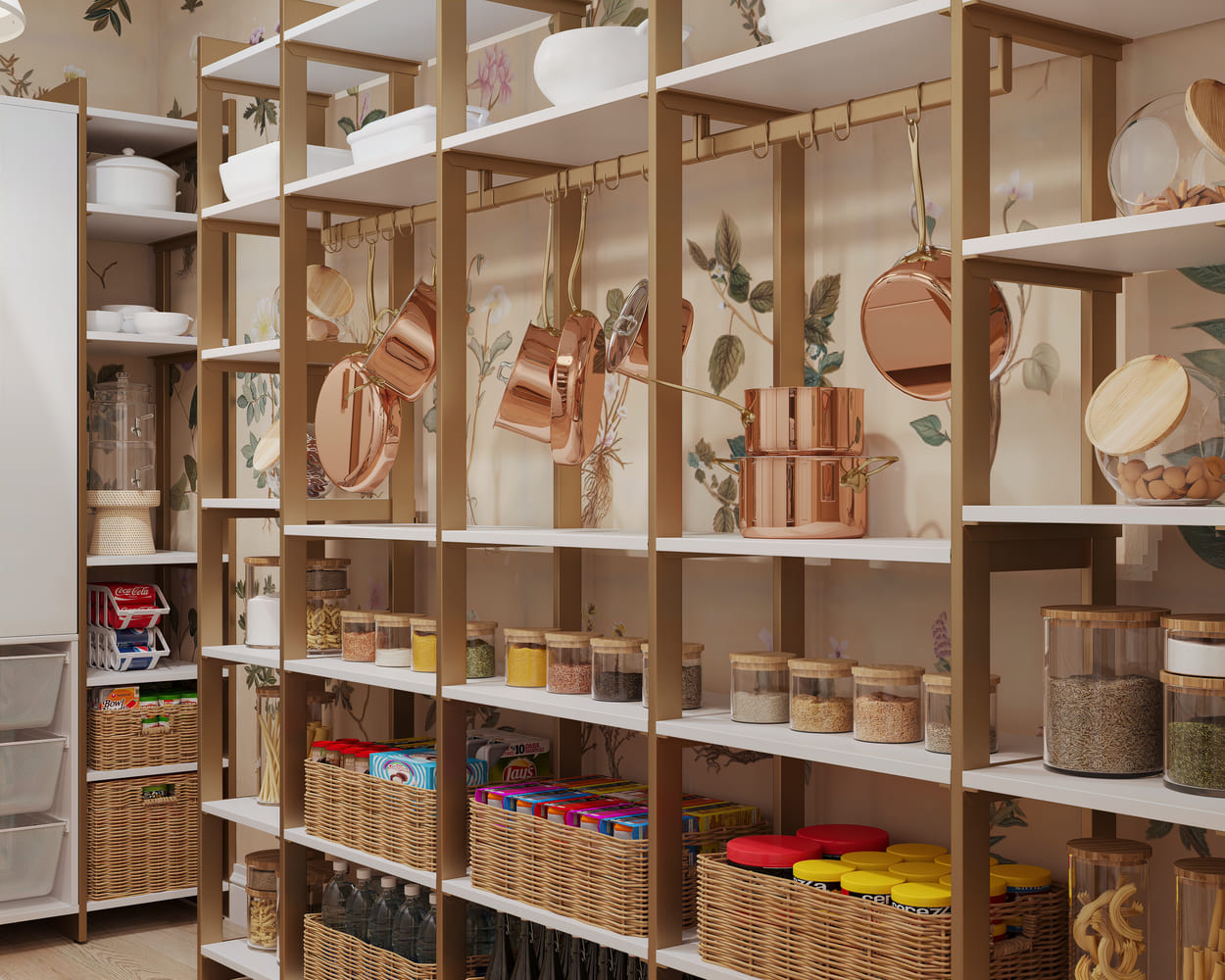

Image from Yousee Studio
The world of interior rendering is dynamic, constantly evolving with emerging technologies and shifting design trends. As we delve into the future of interior rendering, it's clear that several exciting developments are poised to reshape this field even further.
Enhanced Realism with Ray Tracing
One of the most promising advancements in rendering technology is ray tracing. While it's been around for some time, recent hardware innovations and software optimizations are making real-time ray tracing increasingly accessible. This technology offers unparalleled realism by simulating the way light interacts with surfaces. Expect to see interior renderings rival photographs in terms of authenticity, with intricate reflections, refractions, and soft shadows becoming commonplace.
AI-Driven Rendering
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly significant in interior rendering. AI-powered rendering engines can analyze scene compositions, optimize lighting, and suggest design improvements based on user preferences and industry standards. This means faster and more intuitive rendering processes, allowing designers to focus on creativity while AI handles the technical aspects.
Augmented Reality Integration
Augmented reality (AR) is on the cusp of revolutionizing how we perceive interior spaces. Rather than static images, AR will enable designers and clients to experience designs in a fully interactive manner. Expect to see AR apps that allow users to walk through virtual interiors, rearrange furniture with a tap, and even change the color of walls in real time. These immersive experiences will bridge the gap between concept and reality.
Virtual Reality for Design Collaboration
Virtual reality (VR) is making leaps in design collaboration. Designers and clients can meet in virtual spaces to explore designs together. This is particularly valuable for remote associations, as it fosters a sense of presence and immersion that traditional video calls cannot provide. VR will not replace traditional rendering but will complement it, offering an additional interaction layer.
Sustainability Visualization
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in design, rendering tools will evolve to incorporate more sustainability visualization features. This includes showing the carbon footprint of materials, illustrating energy-efficient lighting solutions, and even simulating the impact of natural light on energy consumption. Such features will help designers make eco-conscious choices and communicate sustainability concepts effectively.
Interactive Virtual Design Spaces
Imagine a virtual design studio where clients and designers can interact with virtual prototypes of furniture, fixtures, and materials in real time. This is the future of interior design collaboration. Clients can sit in virtual chairs, open virtual cabinet doors, and feel the texture of virtual fabrics. The ability to make informed decisions about designs without physical prototypes will save time and resources.
Holographic Rendering
While this technology is still in its infancy, holographic rendering can redefine how we perceive interior spaces. Imagine viewing a design as a hologram in your living room, walking around it, and interacting with it as if it were real. While this level of immersion might be some years away, it showcases the futuristic possibilities of interior rendering.
Integration of Real-Time Data
Modern interior renderings can integrate real-time data into designs. This means showing live weather conditions, adjusting lighting based on the time of day, or demonstrating how a space might change with different occupancy levels. Data integration will give clients a more comprehensive understanding of how a design functions in various contexts.
In conclusion, the future of interior rendering promises an exciting fusion of cutting-edge technology, sustainable design, and enhanced collaboration. As these trends evolve, interior designers will be equipped with increasingly powerful tools to bring their creative visions to life and convey their ideas with unprecedented clarity and realism. Interior rendering isn't just a tool for design—it's an art form in its own right, and the canvas is boundless.
Contact us at YouSee Studio for captivating 3D renderings and immersive virtual experiences.
Ray Lisbon is a content writer and the author of this article.